Figure 3.
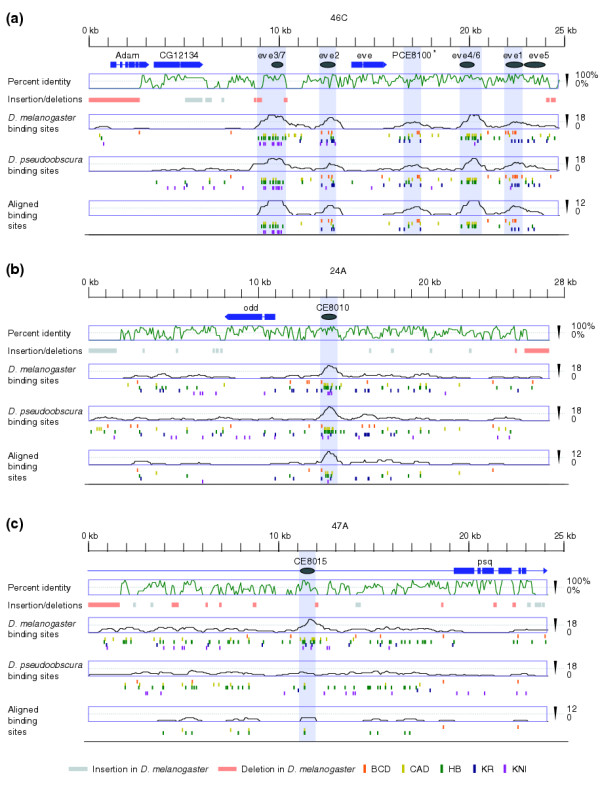
Binding-site conservation, but not sequence conservation, correlates with pCRM activity. Three 25-kb regions were chosen to illustrate patterns of sequence conservation and binding-site conservation. (a)even-skipped (eve) contains five previously known segmentation enhancers (labeled eve3/7, eve2, eve4/6, eve1, and eve5); (b)odd-skipped (odd) contains a single functional (positive) pCRM (CE8010); and (c)pipsqueak (psq) contains a non-functional (negative) pCRM (CE8015). Annotated genes are shown in blue, and the direction of transcription is indicated by the arrow. Gray ovals indicate experimentally tested fragments, and shaded gray boxes show the extent of pCRMs as defined by CIS-ANALYST (minimum of 13 sites within a 700 bp window). The green graphs show average percent identity (in 100-bp windows). Below the percent identity plots are shown insertions (gray boxes) and deletions (orange boxes) of 80 or more bp in the D. melanogaster sequence relative to their D. pseudoobscura ortholog. The location of binding sites in D. melanogaster, binding sites in D. pseudoobscura and aligned binding sites along with the average density of sites (700-bp windows) are shown in the bottom three panels for each region. * in (a) indicates a new prediction (PCE8100).
