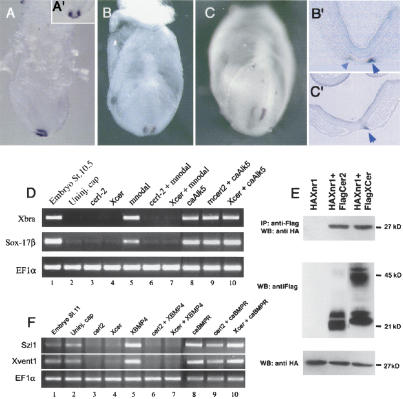
Figure 1.
Biological activity of the asymmetrically expressed cerl-2. (A-C) cerl-2 expression pattern during early mouse development. (A,A′) Lateral and anterior views, respectively, of cerl-2 expression in the node at E7.0. At E7.5 (B), cerl-2 starts to be asymmetrically up-regulated on the right side of the node, and at E8.0 (C) the asymmetry becomes more evident. B′ and C′ show frontal sections of the embryos in B and C, respectively, and provide a detailed view of the perinodal region where cerl-2 is expressed (arrowheads). (D-F) Inhibitory effects of Cerl-2 on Nodal and BMP signaling. (D) cerl-2 inhibits mNodal but not caALK5 mRNA, as assayed by the induction of their target genes Xbra and Sox-17β. (E) Coimmunoprecipitation experiments showing direct binding of Cerl-2 and Xcer to Xnr1. (F) cerl-2 inhibits XBMP4 but not caBr mRNA, as assayed by the induction of their target genes Szl1 and Xvent1.