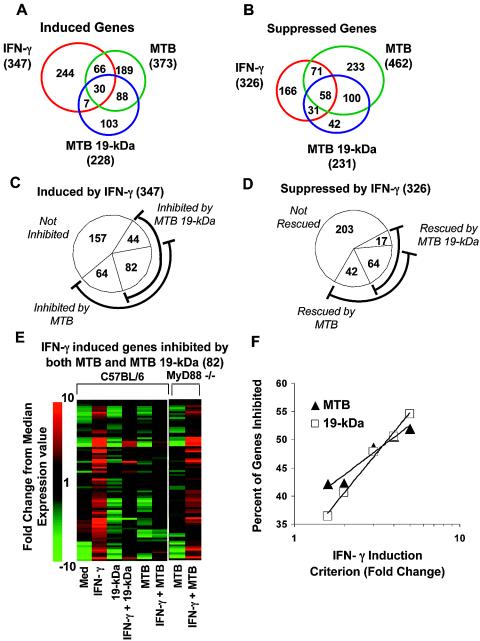
FIG. 2.
Effects of M. tuberculosis and 19-kDa lipoprotein on IFN-γ-induced regulation of macrophage gene expression. Macrophages were incubated for 24 h with or without 30 nM 19-kDa lipoprotein or infected with M. tuberculosis (MOI = 30:1) for 24 h. Cells were then incubated for 15 h with or without 2 ng of IFN-γ/ml in the continued presence or absence of the lipoprotein or M. tuberculosis infection. The baseline sample was macrophages incubated in standard medium. RNA was isolated for microarray analysis. (A and B) Venn diagrams of genes induced (A) or suppressed (B) by IFN-γ, M. tuberculosis, and M. tuberculosis 19-kDa lipoprotein. Numbers below the treatment condition represent the total number of genes induced or suppressed. Numbers within the diagram represent the shared or unique genes induced by these stimuli. A gene was considered induced or suppressed by the stimulus if all nine comparisons were marked increased or decreased with absolute value of a mean fold change of ≥1.6, and the difference in expression values between the two groups was statistically significant based on Welch's t test. (C) Impact of M. tuberculosis and 19-kDa lipoprotein on expression of genes induced by IFN-γ. Inhibited genes were defined as those with decreased or marginally decreased expression in IFN-γ plus M. tuberculosis (or IFN-γ plus 19-kDa lipoprotein) compared to IFN-γ alone in at least five of nine comparisons with a mean fold change less than or equal to −1.2 and a statistically significant difference in expression by using the Welch's t test. (D) Impact of M. tuberculosis and 19-kDa lipoprotein on IFN-γ-mediated gene suppression. A gene was considered rescued if it was marked increased or marginally increased in at least five of nine comparisons with mean fold change greater than or equal to 1.2 and a statistically significant difference in expression as determined by using Welch's t test. (E) Expression patterns of the genes inhibited by both M. tuberculosis and M. tuberculosis 19-kDa lipoprotein. The 82 genes inhibited by both M. tuberculosis and M. tuberculosis 19-kDa lipoprotein were organized by using hierarchical clustering. The relative expression values of the inhibited genes are shown. (F) Genes strongly induced by IFN-γ are more likely to be inhibited by M. tuberculosis and 19-kDa lipoprotein. The x axis shows the fold change criterion used to determine the subset of genes that were induced by IFN-γ (as in Fig. 2A). The y axis shows the percentage of genes determined to be inhibited by either M. tuberculosis or M. tuberculosis 19-kDa lipoprotein (as in Fig. 2C).