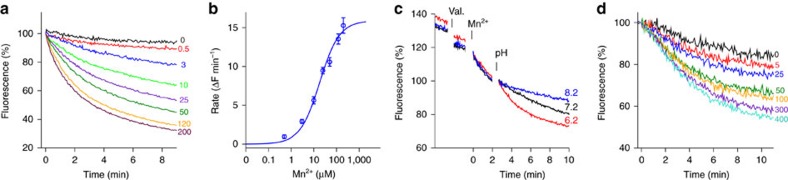
Figure 1. Functional characterization of EcoDMT.
(a) Metal ion transport. EcoDMT mediated Mn2+ transport into proteoliposomes assayed by the quenching of the fluorophore calcein trapped inside the vesicles. Experiments were carried out at pH 7.2. Traces are shown in unique colours with outside Mn2+ concentrations (μM) indicated. (b) Mn2+ concentration dependence of transport. The solid line shows the fit to a Michaelis–Menten equation with an apparent KM of 18.2 μM. Data points represent mean and s.e.m. of 5–9 technical replicates from two independently prepared batches of proteoliposomes. (c) pH dependence of transport. Time dependence of Mn2+ transport at an outside concentration of 4.5 μM. Addition of valinomycin (Val.) and Mn2+ are indicated. Transport was initially assayed at pH 7.2 for all conditions. After two minutes (pH) the pH was adjusted to the indicated value by addition of equivalent volumes of either NaOH, water, or HCl. (d) Proton transport. Mn2+-dependent transport of H+ into proteoliposomes containing EcoDMT. Transport is assayed by the quenching of the pH-dependent fluorophore ACMA at an initially symmetric pH of 7.2. Traces are shown in unique colours with outside Mn2+ concentrations (μM) indicated.