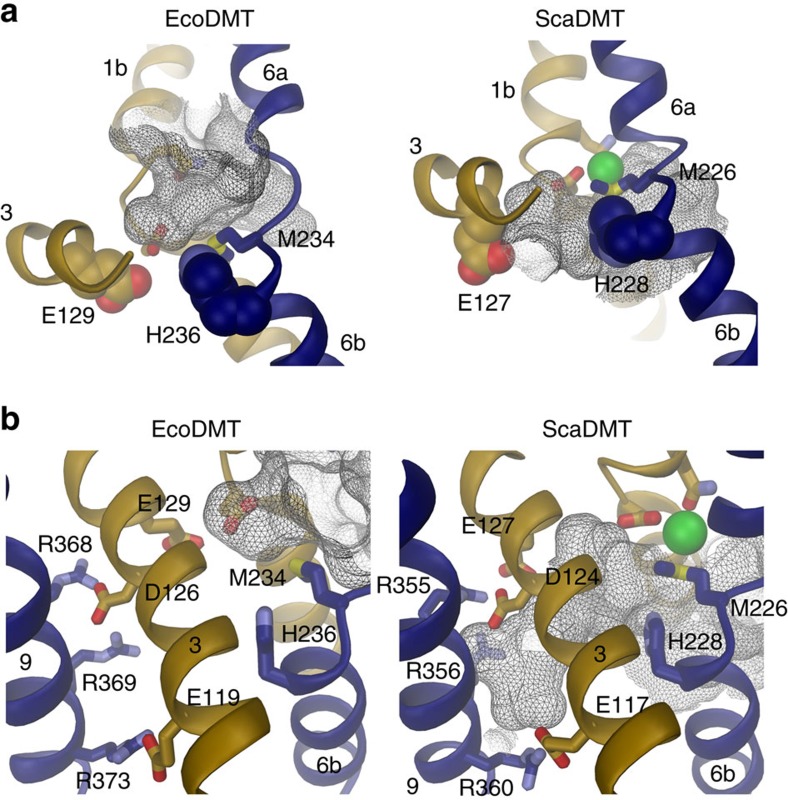
Figure 5. Residues potentially involved in H+ transport.
(a) Location of potential proton acceptors with respect to the ion-binding site of EcoDMT (left) and ScaDMT (right). The side chains of ion coordinating residues are shown as sticks, Glu129 and His236, two potential proton acceptors, as space-filling models. (b) Location of Glu129 and His236 with respect to the aqueous substrate access cavities in EcoDMT (left) and ScaDMT (right). Side chains of ion coordinating residues, the two potential proton acceptors and of conserved acidic and basic residues lining a narrow aqueous cavity in ScaDMT are shown as sticks. In a and b, the molecular surface of aqueous cavities is shown as grey mesh. The green sphere corresponds to the bound Mn2+ in ScaDMT. Selected α-helices are shown as ribbons and labelled accordingly.