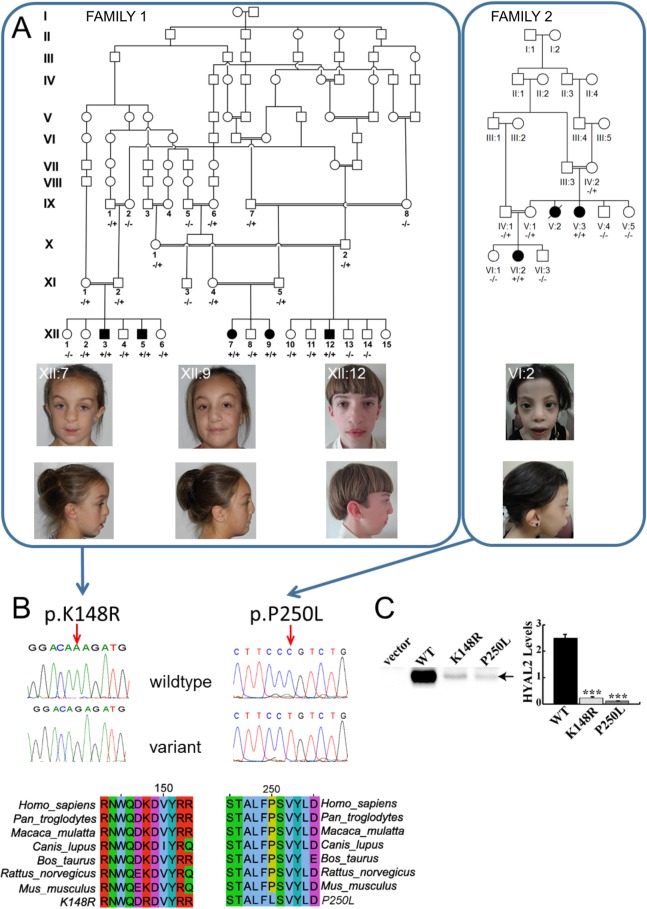
Fig 1. Pedigrees, clinical features of individuals homozygous for HYAL2 mutation and identified HYAL2 mutations, expression of wild type (WT), K148R-HYAL2 and P250L-HYAL2.
(A) Pedigree diagrams and facial phenotype of individuals (Amish Family 1: XII:7; XII:9; XII:12 and Saudi Family 2: VI:2) with HYAL2 deficiency. Note the craniofacial similarities including frontal bossing, hypertelorism, widened nasal bridge, flattened broad nasal tip and cupped ears/overfolding of the superior helices. Consent for publication of these photographs was obtained (B) Electropherograms showing the identified c.443A>G & c.749C>T mutations and conservation of protein sequence across species.(C) Expression of wild type (WT), K148R and P250L-HYAL2. Western blots were performed on lysates prepared from MEFs deficient in HYAL2 that were transfected with empty vector, pCMV6-HYAL2, pCMV6-HYAL2K148R, or pCMV6-HYAL2P250L. An arrow indicates HYAL2. HYAL2 levels shown in the graph were quantified by imaging the chemiluminescent signal using a BioRad ChemiDoc. The columns represent the average level (x 106 light units) of HYAL2 ± SEM (n = 4). Significance was determined using the student’s T test. *** indicates p<0.0001.