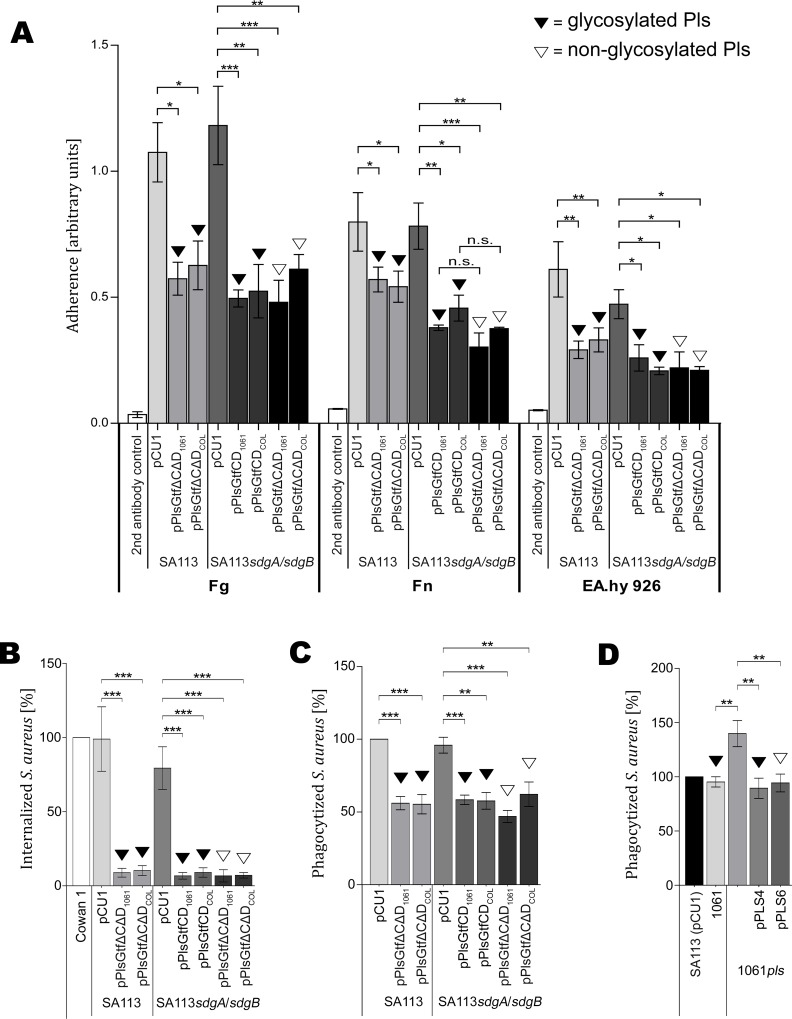
Fig 7. Functional characterization of Pls glycosylation.
(A) Pls reduces the adherence of S. aureus to Fg, Fn, and endothelial cells independently of its glycosylation status. The wells of microtiter plates were coated with Fg, Fn or endothelial cells, blocked, and incubated with the bacteria. After washing, binding was assessed as arbitrary units in ELISA adherence assays. Results are shown as the mean of three independent experiments. Statistical significance is marked by asterisks. (B) Pls reduces the internalization of S. aureus by endothelial EA.hy 926 cells independently of its glycosylation status. The internalization of FITC-labeled S. aureus strains by adherent EA.hy 926 cells was assessed by flow cytometry and computed in relation to S. aureus strain Cowan 1, which was set to 100% internalization. Data are shown as the mean of three independent experiments. Statistical significance is marked by asterisks. (C, D) Pls reduces the phagocytosis of S. aureus by PMNs independently of its glycosylation status. The phagocytosis of FITC-labelled S. aureus strains by PMNs was assessed by flow cytometry and computed in relation to S. aureus SA113 (pCU1), which was set to 100%. Data are shown as the mean of three independent experiments. Statistical significance is marked by asterisks.