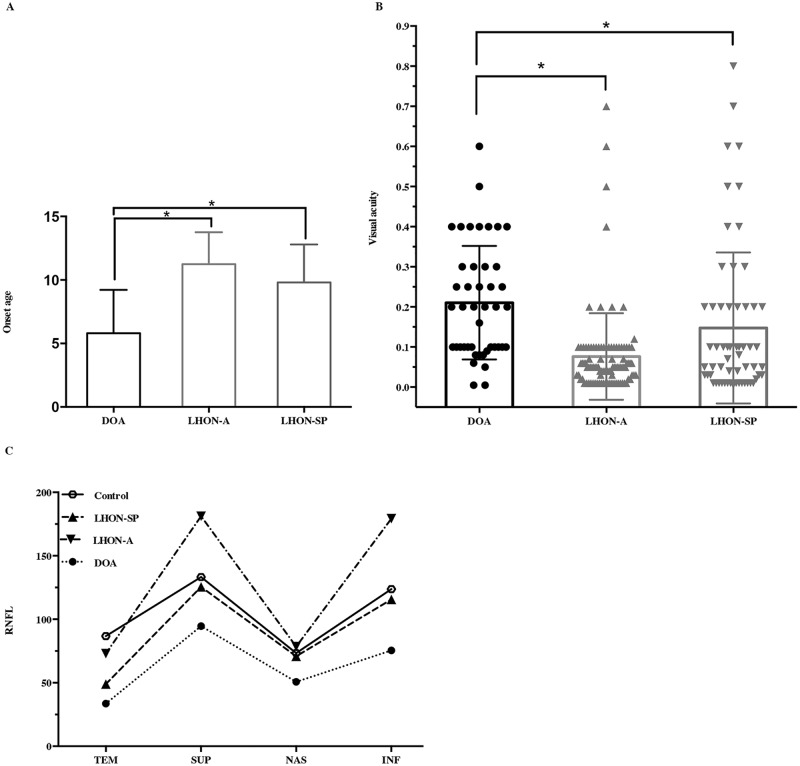
Fig 1. Comparison of the onset age, visual acuity and RNFL thickness in the DOA and LHON (LHON-A and LHON-SP) groups.
(A) Comparison of the onset ages of the DOA, LHON-A and LHON-SP: (a) DOA at preschool age; (b) LHON-A and LHON-SP groups at school age; (c) the onset age of DOA was statistically younger than LHON-A (P < 0.001) and LHON-SP (P < 0.001). * The onset age of DOA was earlier than patients with LHON-A (P < 0.001) and LHON-SP (P < 0.001). (B) Comparison of the visual acuity among DOA, LHON-A and LHON-SP: (a) The visual acuity of LHON-A was worse than LHON-SP; (b) The visual acuity of DOA was significantly better than LHON-A and LHON-SP. * The visual acuity of patients with OPA1 mutations was significantly better than patients with LHON-A and LHON-SP (P < 0.001). (C) Comparison of RNFL thickness in four quadrants among patients with OPA1 mutations, LHON-A, LHON-SP and controls using one-way ANOVA: (a) The RNFL was thinner in all four quadrants of DOA. (b) The RNFL thickness of LHON-A group was statistically thicker in superior and inferior quadrants, but there were no obvious differences in the temporal and nasal quadrants. (c) The RNFL thickness of LHON-SP was significantly thinner in the temporal quadrant, but there were no significant differences in the other three quadrants. DOA: patients with OPA1 mutations; LHON-A: patients with LHON presented with optic edema or hypaeremia with tortuous vessels. LHON-SP: patients with LHON presented with optic pallor or atrophy.