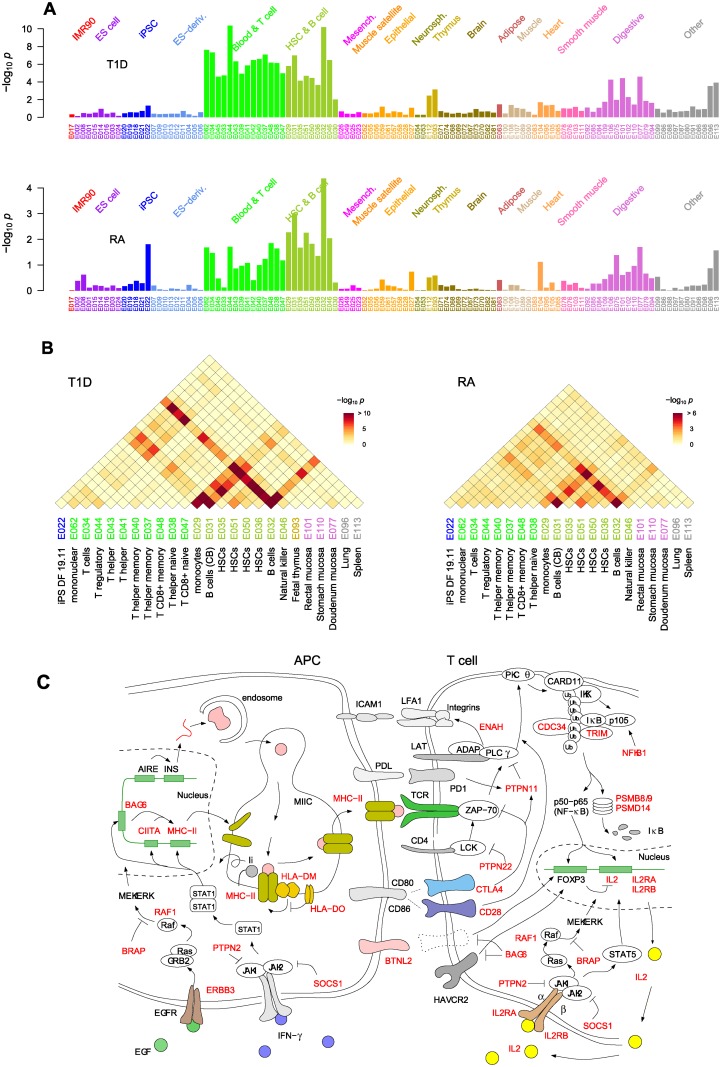
Fig 4. Cell type-specific enrichment of SNPs and their interactions.
(A) Single-SNP enrichment (over-representation p-values) of T1D and RA-associated proxy SNPs (Fig 2) in reference epigenomes. (B) Enrichment of statistically significant interaction pairs active in cell type combinations. Combinations with negligible enrichment are not shown for clarity. Note the dominance of B cells in their interaction to T cells, monocytes, and intestinal epithelial cells. See S5 Fig for the full epigenome names. (C) Interrelationships of genetic factors associated with autoimmunity in the context of antigen presenting cell (APC) versus T cell interaction. Thymic APCs are stimulated by the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and interferon (IFN)-γ signaling pathways to express major histocompatibility (MHC) class II molecules, which are assembled in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and loaded by AIRE-induced self-peptides in the endosomal MHC class II compartment (MIIC). The peptide-MHC complex is recognized by the T cell receptor (TCR), initiating its downstream signaling leading to the activation of NF-κB, which enters the nucleus and up-regulates FOXP3 (in Tregs), interleukin (IL)-2 receptors, and IL-2 (in conventional CD4+ T cells). IL-2 signaling is crucial to both conventional T cell proliferation and Treg cell activation. Genes shown in red are those implicated by the top-ranked pathways (Fig 6).