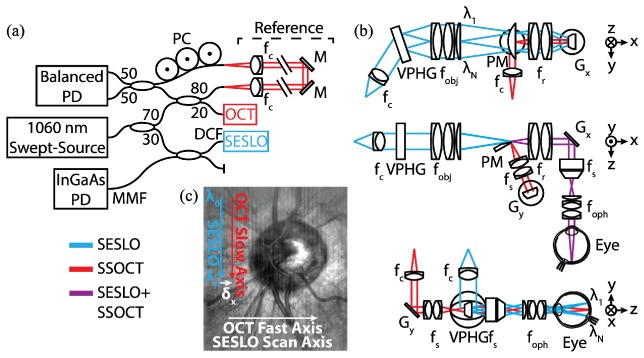
Fig. 1.
SS-SESLO-OCT engine and imaging optics schematics. (a) A 1060 nm swept-source is shared between the SESLO and OCT via a 30:70 coupler, respectively. SESLO illumination is relayed by the single-mode core and detected by the multimode inner cladding of a prototype DCFC. (b) Cross-sectional views of the imaging optics (SESLO, blue; OCT, red; shared, purple). SESLO and OCT optical paths share a scanning mirror (Gx, SESLO scan axis and OCT fast axis) and are combined using a pick-off mirror. (c) Representative in vivo retinal SESLO image centered on the optic nerve showing: SESLO encoded, SESLO scan, OCT fast, and OCT slow axes. The SESLO and OCT FOVs are offset in the fast axis by ~25 μm at the retina (δx). DCF, double-clad fiber; f, collimating, objective, ophthalmic, relay, and scan lenses; Gx,y, galvanometer scanners; M, mirror; MMF, multimode fiber; PC, polarization controller; PD, photodiode; PM, D-shaped pickoff mirror; VPHG, grating.