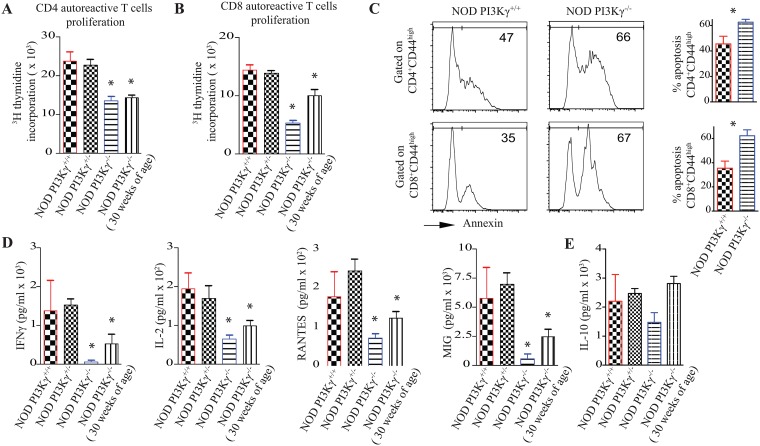
Fig 3. PI3Kγ-deficiency impairs autoreactive-T-cells activation and survival upon stimulation with pancreatic-peptides.
(A) Graph represents autoreactive CD4 T-cell proliferation for 48 hours as measured by thymidine incorporation. Splenocytes recovered from NOD.PI3Kγ+/+, NOD.PI3Kγ+/-, NOD.PI3Kγ-/- at 12-weeks of age and NOD.PI3Kγ-/- at 30-weeks were stimulated ex-vivo with BDC2.5 pancreatic peptide. (B) Graph represents autoreactive CD8 T-cell proliferation as measured by thymidine incorporation. Splenocytes recovered from NOD.PI3Kγ+/+, NOD.PI3Kγ+/-, NOD.PI3Kγ-/- at 12-weeks of age and NOD.PI3Kγ-/- at 30-weeks were stimulated ex-vivo with IGRP pancreatic peptide. (C) Representative examples of apoptosis analysis by flow-cytometry on CD4 and CD8 effector-T-cells 2 days after stimulation with pancreatic-peptides. CD4 and CD8 effector-T-cells (CD44high) of NOD.PI3Kγ-/- went more into apoptosis as measured by annexin expression compared to WT-NOD.PI3Kγ+/+. (D and E) Graphs represent cytokines analysis as measured by Luminex-assay on supernatant from an ex-vivo BDC2.5 pancreatic peptide challenge of splenocytes recovered from the different mice. (*p<0.05, n = 4 mice/group). As shown in panels A and B autoreactive-T-cells from the NOD.PI3Kγ-/- proliferated less and produced less inflammatory cytokines compared to NOD.PI3Kγ+/+, NOD.PI3Kγ+/-. (*p<0.05, n = 4 mice/group).