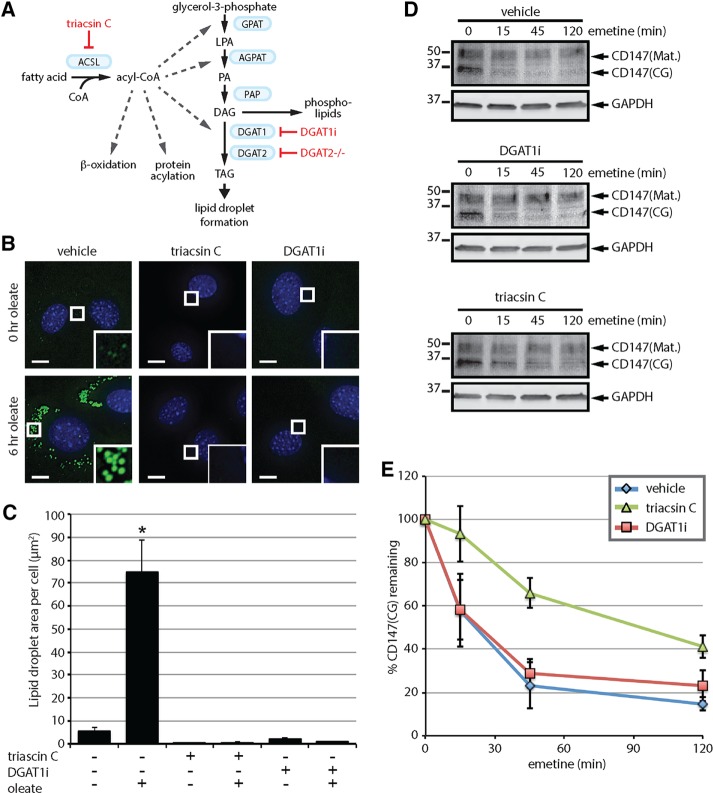
FIGURE 5:
Lipid droplet biogenesis is dispensable for CD147 ERAD. (A) The Kennedy pathway of TAG synthesis indicating the enzymes (blue boxes) and metabolites. Select additional pathways that use acyl-CoA are also depicted. Approaches to disrupt LD biogenesis through the inhibition of ACSLs (triacsin C) or the DGAT enzymes (DGAT1i and DGAT2-/-) are indicated in red. (B) DGAT2-/- MEFs were pretreated with 1 µg/ml triacsin C or 20 µM DGAT1i for 3 h and then incubated with 200 µM oleate for 0 or 6 h as indicated. Fluorescence microscopy was employed to visualize LDs (green) and nuclei (blue). Scale bar, 5 µm. (C) The abundance of LDs was quantified from cells treated as shown in B. Asterisk indicates a significant increase in LD amount relative to untreated cells (p < 0.05). (D) DGAT2-/- MEFs were pretreated with vehicle, 1 µg/ml triacsin C, or 20 µM DGAT1i for 16 h, followed by 75 µM emetine for the indicated times. CD147 levels were assessed by immunoblotting of SDS lysates. (E) The relative levels of CD147(CG) in D were quantified and are presented as percentage of the levels at time 0 h (n = 3). ACSL, long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase; AGPAT, acylglycerolphosphate acyltransferase; DAG, diacylglycerol; DGAT, diacylglycerol acyltransferase; GPAT, glycerol-phosphate acyltransferase; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; PA, phosphatidic acid; PAP, phosphatidic acid phosphatase; TAG, triacylglycerol. Error bars indicate SEM.