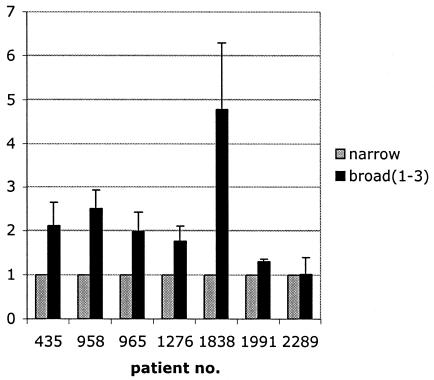
FIG. 5.
Comparison of the infectivities of sequential R5narrow and R5broad(1) to R5broad(3) isolates from seven patients. A plaque assay with U87.CD4-CCR5 cells was used, and titers were determined at the same time with the same amount of p24 antigen per volume of virus supernatant. A pairwise comparison of sequential isolates with different R5 phenotypes was performed. Results are shown as ratios of numbers of plaque-forming units of R5broad(1), R5(broad2), and R5(broad3) isolates to R5narrow isolates per milliliter, where the infectivity of R5narrow was set at 1. Error bars show intra-assay variation. Infectious titers of R5broad(1), R5(broad2), and R5(broad3) isolates were significantly higher than those of isolates with the R5narrow phenotype (P = 0.04, Wilcoxon signed-rank test).