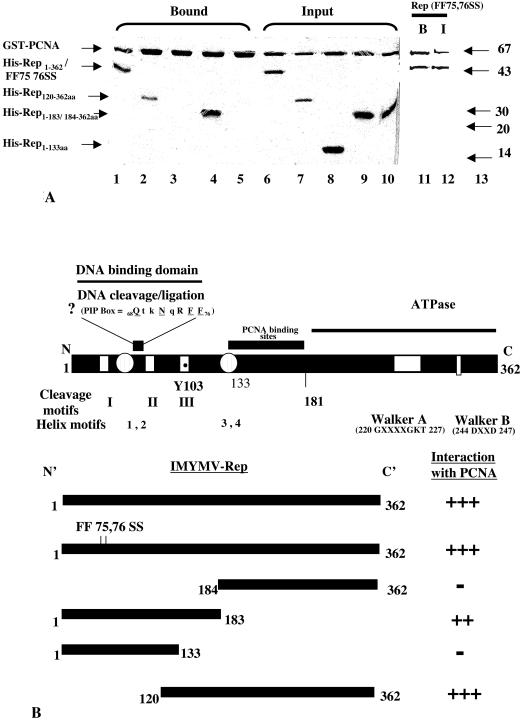
FIG. 5.
Delimitation of the Rep zone for interactions with PCNA. (A) In vitro associations of various deletion derivatives of Rep with recombinant tobacco PCNA. A Coomassie blue-stained SDS-12.5% polyacrylamide gel shows purified input proteins for GST-PCNA and six-His-tagged Rep (lanes 6 to 10). Lane 1 shows the full-length wild-type six-His-tagged Rep protein bound to GST-PCNA. Bound six-His-tagged Rep120-362aa and six-His-tagged Rep1-183aa are shown in lanes 2 and 4, respectively. Six-His-tagged Rep1-133aa and six-His-tagged Rep184-362aa are shown in input lanes (lanes 8 and 10) but not as bound and eluted proteins (lanes 3 and 5). Lanes 11 and 12 show bound (B) and input (I) six-His-tagged Rep1-362aa (FF75,76SS), respectively. Molecular mass standards (in kilodaltons) are shown in lane 13. (B) Various domains and motifs of IMYMV Rep and summary of IMYMV Rep and PCNA interactions. Various domains of Rep and the corresponding coordinates are indicated in the upper panel. The active residue (Y) of nicking-closing activity is shown. The nonfunctional PIP box is shown in an expanded manner; conserved residues are underlined. Interaction characteristics are summarized in the bottom panel; +++, ++, and − indicate the degrees of interactions (+++ and ++, presence; −, absence).