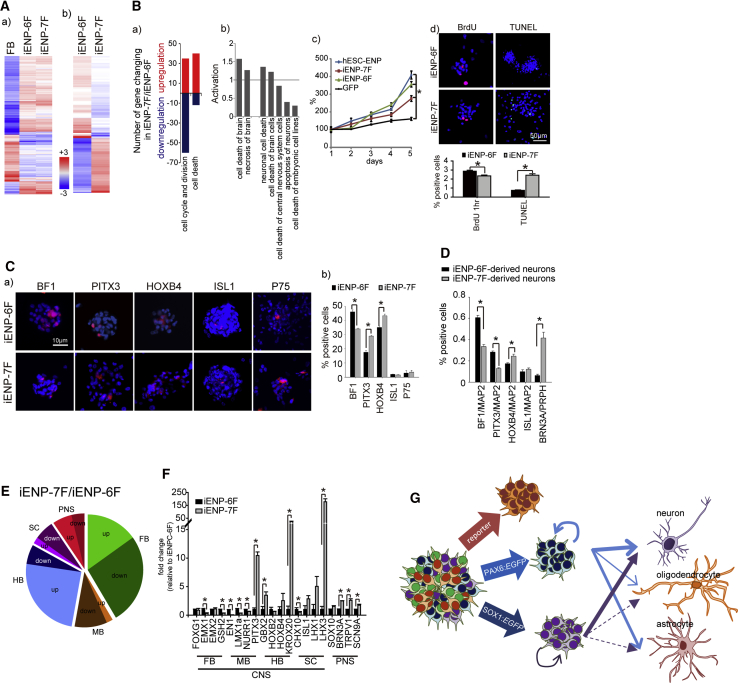
Figure 6.
The Differential Properties of iENP-6F and iENP-7F
(A) Heatmap analysis of global gene expression profiles of undifferentiated iENP-6F, iENP-7F, and FBs.
(B) (a) Dynamic changes in the expression of genes characterized by the indicated GO terms. Red, upregulated; blue, downregulated. (b) IPA of the activated pathways associated with cell death. (c) Growth curve analysis of the indicated cell populations. (d) ICC staining and quantification of iENPs by BrdU incorporation and TUNEL assays. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue).
(C) Preferential expression of brain regional markers in iENPs. (a) ICC staining of iENPs with antibodies against brain regional antigens, as indicated. (b) Quantification of the percentage of cells expressing brain regional markers, as indicated, in iENPs.
(D) Quantification of the percentage of cells expressing the indicated brain regional markers in iENP-derived neurons.
(E) Pie chart depicting the proportion of brain regional subtype-associated genes up- and downregulated between iENP-7F and -6F.
(F) Relative expression of brain regional-associated genes in iENP-7F and -6F, as measured by RT-qPCR analysis.
(G) Model illustrating the strategy for direct conversion of iENPs with differential differentiation propensities through the use of different combinations of hESC-ENP-TFs and neural reporters.
FB, forebrain; MB, midbrain; HB, hindbrain; SC, spinal cord. The weight of the solid/dashed arrow indicates the neural differentiation potential of the iENP populations.
All quantitative data were obtained from three independent experiments and are presented as means ± SD. ∗p < 0.05.