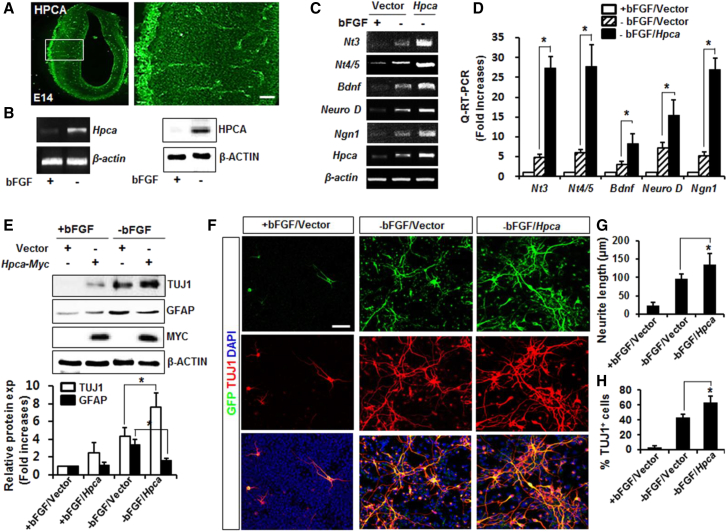
Figure 1.
Effect of HPCA Expression during Neuronal Differentiation of NSCs
(A) HPCA immunostaining of coronal sections of E14 rat brain cortex. The boxed area is magnified. Scale bar, 20 μm.
(B) Neuronal differentiation was induced by removal of bFGF for 1 day, and Hpca mRNA expression was analyzed by RT-PCR. Twenty micrograms of protein was analyzed by western blotting with anti-HPCA and anti-β-ACTIN.
(C and D) NSCs were transfected with pMSCV-IRES-EGFP or pMSCV-IRES-EGFP-Hpca-Myc for 48 hr and allowed to differentiate for 24 hr. mRNA levels of neuronal factors were analyzed by RT-PCR (C) and real-time RT-PCR (D). ∗p < 0.05 compared with the −bFGF/vector control (mean ± SD; n = 3).
(E) Cells were transfected with pMSCV-IRES-EGFP or pMSCV-IRES-EGFP-Hpca-Myc for 48 hr and induced to differentiate for 24 hr. Levels of TUJ1, GFAP, MYC, and β-ACTIN were determined by western blot. ∗p < 0.05 compared with the −bFGF/vector control (mean ± SD; n = 3).
(F) Cells were transduced with pMSCV-IRES-EGFP or pMSCV-IRES-EGFP-Hpca-Myc and induced to differentiate by withdrawal of bFGF. After 3 days, GFP-positive cells were examined by fluorescence microscopy and stained with anti-EGFP (green) and anti-TUJ1 (red). Scale bar, 20 μm.
(G and H) Neurite lengths were measured and the proportions of TUJ1-positive cells and total cells were determined in randomly selected areas from at least three slides of each condition. ∗p < 0.05 compared with the −bFGF/vector control (mean ± SD; n = 3).