Figure 6.
Functionally Divergent Activity of the Alternatively Spliced Variants of Hlf and Pbx1
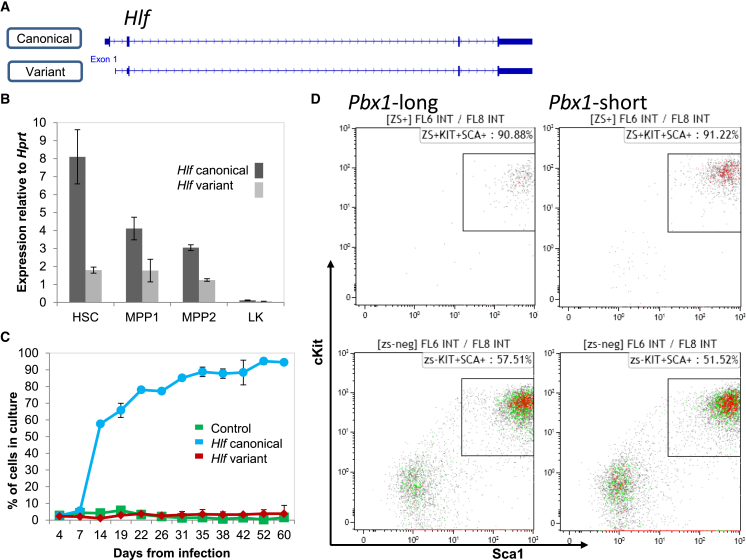
(A) Schematic of the Hlf gene.
(B) Expression of Hlf variants 1 and 2 (Hlf1 and Hlf2) relative to Hprt in mouse HSCs in two types of multipotent progenitors (MPP1 and MPP2), and in a population of committed progenitors (Lineage-cKit+Sca1-, sometimes called LK cells). Data of technical triplicate average ± SD from one representative experiment out of four are shown.
(C) Hlf1 provides a growth advantage in culture compared with Hlf2. Graph showing frequencies of Hlf1 (blue), Hlf2 (red), and reporter-only controls (green) in separate cultures over time. Hlf1 increased in frequency over time, as reported by Gazit et al. (2013), whereas Hlf2 did not. Data of technical duplicate average ± SD from one representative experiment out of five are shown.
(D) Both canonical (Pbx1-long) and variant (Pbx1-short) forms of Pbx1 increase cKit and Sca1 expression in vitro. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting plots of cells overexpressing the indicated factor (top panels) or controls (bottom panels) show the frequencies of cKit+Sca1+ in primary cells after 4 weeks in vitro. Representative data are shown for one of three independent experiments. Control vectors are identical to Pbx1 vectors with the exception of the coding sequence. Plots are representative from one experiment out of three.