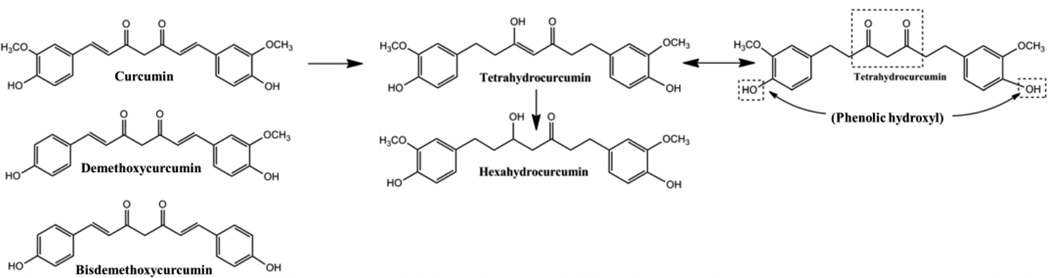
Figure 1.
Chemical structures for curcuminoids. Curcumin is metabolized first to tetrahydrocurcumin, then to hexahydrocurcumin. Tetrahydrocurcumin exists in two forms, due to its keto-enol structure. Curcumin glucuronidation forms a major phenolic and minor alcoholic glucuronides, whereas hexahydrocurcumin, the major curcumin reduction metabolite, forms only a phenolic glucuronide. Demethoxycurcumin forms phenolic and alcoholic glucuronides equally, while bisdemethoxycurcumin primarily forms an alcoholic glucuronide. Curcuminoids are also known to be extensively sulfated.