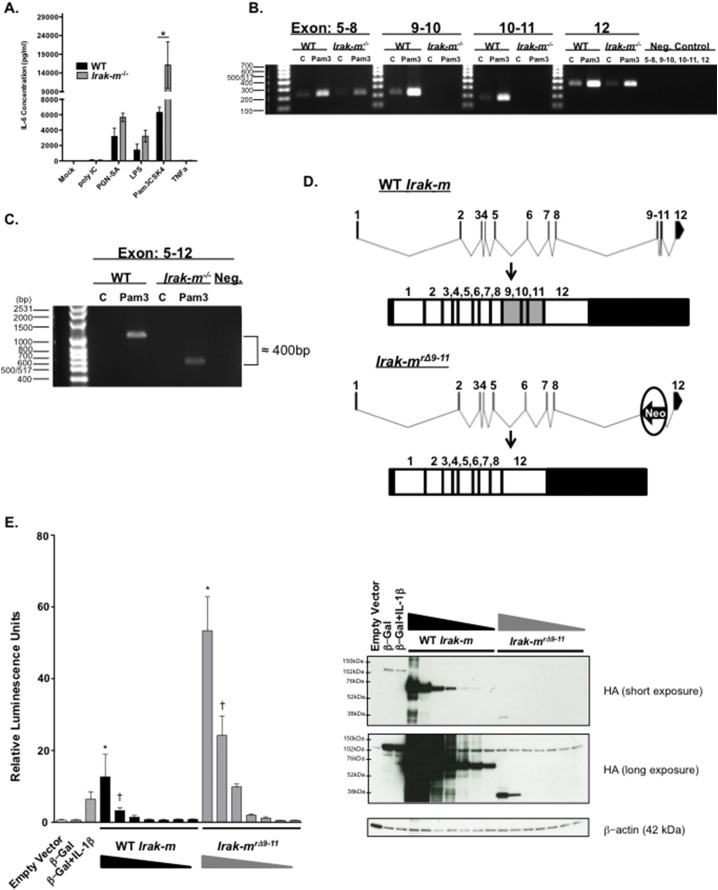
Fig. 6.
Disruption of the murine Irak-m locus results in the formation of an Irak-mrΔ9–11 splice variant. A. Bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) from Irak-m−/− mice demonstrate increased production of IL-6 following 24 h stimulation with specific PAMPs. Data shown are pooled from 3 separate and independent experiments. n = 3 mice per genotype. B. Disruption of the Irak-m locus resulted in the loss of Exons 9–11. BMDM from WT and Irak-m−/− littermates were un-stimulated or stimulated for 24 h with Pam3CSK4. After 24 h, cells were harvested for RNA and RT-PCR was utilized to amplify Irak-m corresponding to exons: 5–8, 9–10, 10–11 and 12, respectively. C. A size difference was detected in the RT-PCR product corresponding to Exons 5–12 between WT and Irak-m−/− BMDMs treated for 24 h with Pam3CSK4. The shift of approximately 400 nucleotides in the Irak-m−/− BMDMs corresponds to the deleted exons 9, 10 and 11. D. Sequencing of the exon 5–12 RT-PCR product revealed a splice immediately after exon 8 together with exon 12. Normal splicing occurs in the WT BMDM, whereas Irak-m−/− BMDM splice around the inserted Neo-cassette after exon 8 and generates a splice variant connecting exon 8 with exon 12. E. (Left) Dual-Luciferase assay of HEK293T cells transfected for 24 h with equal amounts of NF-κB-firefly luciferase reporter plasmid and decreasing amounts of either CMV-WT Irak-m-HA plasmid (625 ng–10 ng) or CMV-Irak-mrΔ9–11-HA plasmid (2500 ng–40 ng) from three independent and pooled experiments. Empty Vector is shown as a negative control. β-Galactosidase-HA is shown as a positive control for transfection. A separate β-Galactosidase-HA transfection was treated with 10 ng/mL human IL-1β for 6 h following 18 h of transfection, and serves as a positive control for NF-kB-firefly luciferase activation. All treatment groups received a constant amount of plasmid DNA described in the Supplemental Experimental Methods and are normalized to the Renilla luciferase activity. (Right) Representative western blot of WT IRAK-M and IRAK-MrΔ9–11 protein expression. Overexpression inserts are HA-tagged at the C-terminus and β-actin is shown as a loading control. The WT IRAK-M expresses readily as seen in the short exposure and migrates at ~ 68 kDa. The IRAK-MrΔ9–11 protein is present in the long exposure migrating at ~ 38 kDa. Data in panel A. is represented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 by 1 way ANOVA, Tukey-Kramer post-test. Data in panel E. is represented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.001, †p < 0.01 by 1 way ANOVA, Tukey-Kramer post-test. Statistical significance between all treatment groups in E is not shown for simplicity. A minimum of 3 independent experiments were conducted for all assays.