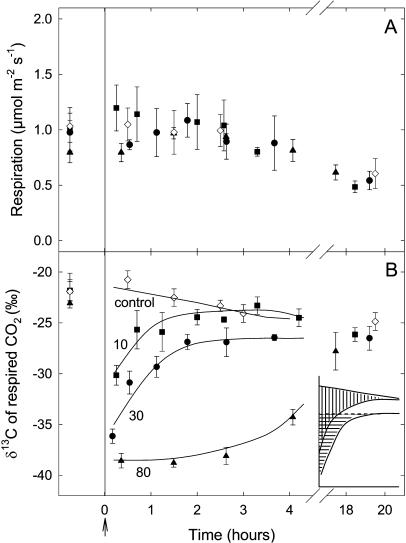
Figure 1.
Changes in the respiration rate (μmol m−2 s−1; A) and δ13C (‰; B) of CO2 respired in the dark after isotopic labeling in French bean leaves. Leaves were labeled with commercial CO2 with δ13C of −51.2‰ for 20 min (10 mmol C fixed per m2; squares), 75 min (30 mmol C fixed per m2; circles), and 180 min (80 mmol C fixed per m2; triangles), respectively. The arrow indicates the beginning of the dark period. The δ13C value of the dark-respired CO2 for a 20-h dark period for unlabeled leaves is also shown (diamonds). Data are the means of three replicates (se values are shown when larger than the symbols). At the beginning of the dark measurements, the percent of new carbon in respired CO2 was 18%, 29%, and 34% for the 10, 30, and 80 mmol C m−2 labeling curves, respectively. Inset, Schematic drawing of the surfaces delimited by (1) the control δ13C and the δ13C of the 20-min labeling (10 mmol C fixed per m2) curves; and (2) the δ13C of the 75-min labeling (30 mmol C fixed per m2) curve and the steady-rate line (δ13C = −27‰).