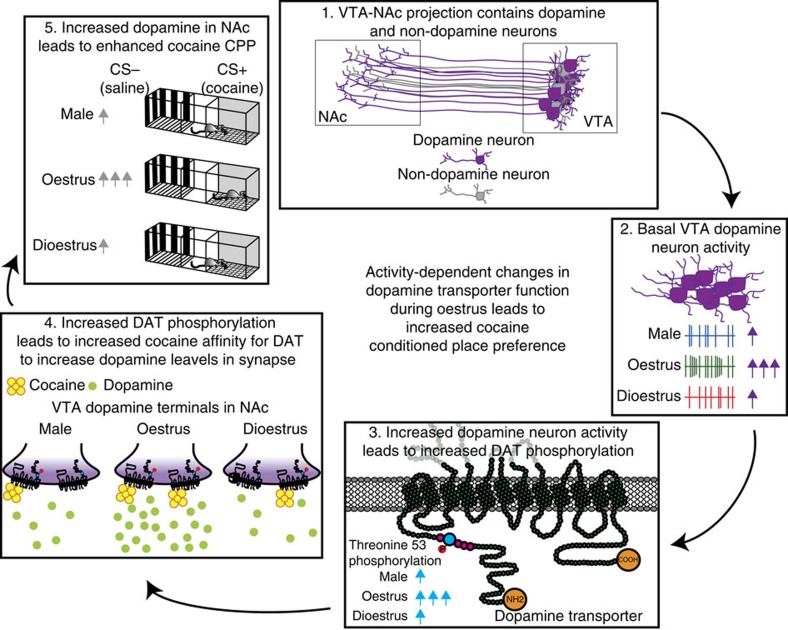
Figure 6. Proposed schematic highlighting a potential mechanism for the activity-dependent changes in reward processing that occur during oestrus.
(1) The VTA to NAc pathway comprises dopaminergic neurons (purple) and other neuronal subpopulations (grey). (2) Dopamine neuron firing is enhanced during oestrus. (3) The increased activity of this pathway leads to downstream ERK activation and concomitant phosphorylation of Thr53 (blue) on DAT. (4) These changes in DAT lead to alterations in cocaine affinity, whereby cocaine is more able to bind to DAT and increase extracellular dopamine levels. This increased cocaine binding leads to increased dopamine levels in the NAc. (5) In vivo this drives increased associations between cocaine and contextual cues, which leads to enhanced cocaine CPP due to differences in the perceived rewarding value of cocaine.