Fig. 5.
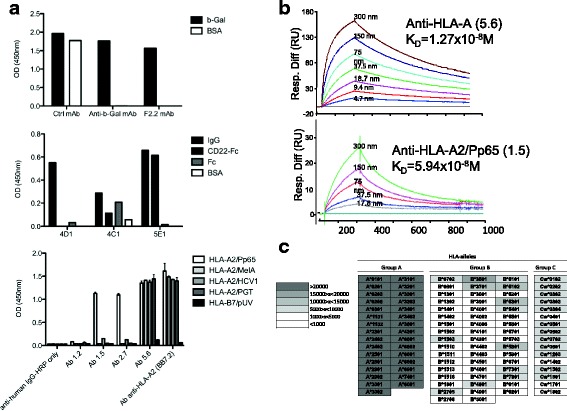
Specificity and affinity of mAbs generated from human immunoglobulin transgenic rats single B cells. a Specificity ELISA of mAbs generated from human immunoglobulin transgenic rats immunized with β-Gal (upper panel), CD22 (middle panel) and HLA-A2/Pp65 (lower panel). Upper panel: a representative anti-β-Gal specific mAb (F2.2) among those generated, a control mAb that nonspecifically binds to different proteins (Ctrl mAb) and a positive control human anti-β-Gal mAb previously generated by us [11]. Middle panel: 4D1 mAb did not recognize any epitope on CD22-Fc fusion-protein, 4C1 mAb recognized an epitope on the Fc domain of the fusion-protein, whereas 5E1mAb specifically recognized the CD22 protein. Lower panel: mAbs 1.5 and 2.7 recognized only the HLA-A2/Pp65 monomer, mAb 5.6 recognized all monomers containing the HLA-A2 molecule and anti-HLA-A2 mAb clone BB7.2 was added as a positive control. b Determination of the affinity of mAbs 5.6 and 1.5 generated from human immunoglobulin transgenic rats immunized with HLA-A2/Pp65 using surface plasmon resonance by flowing various concentration of HLA-A2/Pp65 complexes over CM5 chip-bound mAb. c Analysis of the specificity of mAb 5.6 in a Luminex single antigen bead assay. Results are shown in terms of interval MFI. Positivity threshold was set at 1000
