Fig. 7.
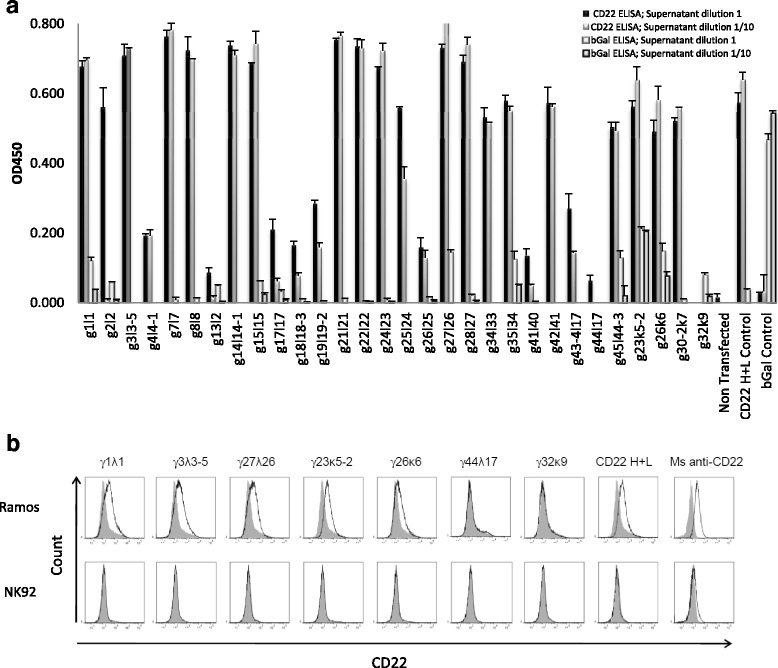
CD22 specificity analysis of antibodies by ELISA and flow cytometry. Supernatants from HEK 293 cells transfected with light and heavy chain coding constructs from single anti-human CD22 B cells were analysed for reactivity against human CD22. a Human CD22 or β-Gal were coated at a concentration of 5 μg/mL in 96-well plates. 50 μL of IgG expression supernatants collected 5 days after transfection were used pure or diluted at 1:10 in PBS and used as the primary antibody. Biotin conjugated anti human IgG H + L antibody was used as the secondary antibody. Streptavidin HRP was used for detection. OD450 read from blank control was deducted from all wells. Cell culture supernatants from human anti-β-Gal H + L (clone 44A8, β-Gal Control) and CD22 H + L (clone 5E1, CD22 H + L Control) transfected cells were used as positive controls in β-Gal and CD22 ELISA, respectively. Non-transfected cell culture supernatant was used as the negative control. b Representative flow cytometry analysis of heavy and light chain co-transfected HEK cell culture supernatants. Supernatants from the indicated heavy + light chain positive transfections in ELISA (the first 5 from left) or negative (the following ones) and were used as primary antibodies on Ramos CD22+ and NK92 CD22− cell lines. Cell culture supernatants from human anti-CD22 H + L (clone 5E1, CD22 H + L) transfected cells and a commercial mouse mAb anti-human CD22 (Ms anti-hu CD22) were used as positive controls. Biotin conjugated anti human IgG H + L antibody was used as a secondary antibody and streptavidin Alexa405 was used for cytometry detection. Histograms for transfected cell supernatant shown in black non-transfected cell supernatant in filled grey. Control Ramos and NK92 cell lines were labelled with a commercial mouse anti human CD22 FITC (black line) or with an isotype control (filled grey)
