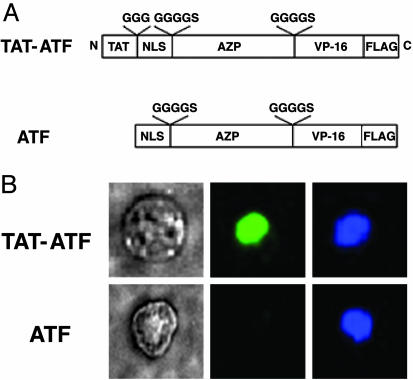
Fig. 2.
Immunofluorescent staining of TAT-ATF and ATF in HEK293 cells. (A) Schematic representation of DRPs used in this study. A cell-penetrating peptide, TAT, was fused to an artificial transcription factor (ATF) comprising a NLS, a six-fingered AZP, a VP-16 activation domain, and a FLAG epitope tag to yield a TAT-ATF. The amino acids shown above the open boxes are linker peptides. (B) Visualization of DRPs transduced into HEK293 cells by immunofluorescent assay. HEK293 cells (2 × 104) were treated with 2 μM TAT-ATF (Upper) or ATF (Lower) for 2 h at 37°C, and the transduced proteins were identified by immunofluorescent staining as described in Materials and Methods. Phase-contrast image of a 293-H cell (Left) and a fluorescence image of the same cell stained with an anti-FLAG antibody-FITC conjugate (Center) are shown. The nucleus of the cell was also labeled with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride (DAPI) (Right).