Fig. 6.
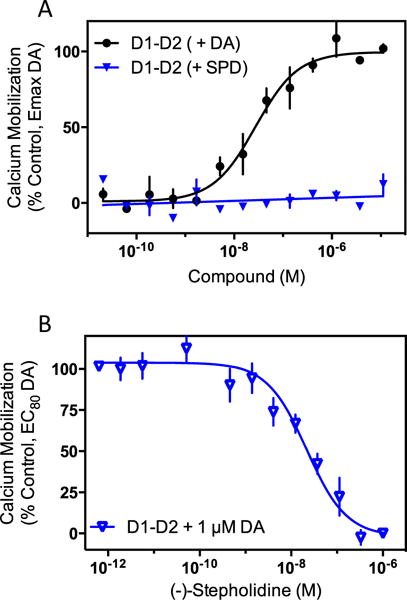
(−)-Stepholidine is an antagonist of dopamine-stimulated D1RD2R dimer-dependent intracellular calcium mobilization. a HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with D1R and D2R and then tested for calcium mobilization using a live cell-based assay as described in the “Materials and methods” section. Dopamine (DA) stimulated intracellular calcium mobilization (EC50=32.3±13.2 nM, n=3), whereas (−)-stepholidine (SPD) did not produce a calcium response. Neither compound produced a response in non-transfected, or in D1R- or D2R-only transfected cells (data not shown). Data are expressed as the % maximum dopamine response. b The same cells were assayed for inhibition of dopamine-stimulated calcium mobilization using an EC80 (1 μM) concentration of dopamine. (−)-Stepholidine inhibited dopamine-stimulated calcium mobilization in cells co-transfected with the D1R and D2R (IC50=19.3±3.7 nM, n=3). Data are means of three independent experiments and are expressed the as the percent stimulation of the EC80 concentration of dopamine
