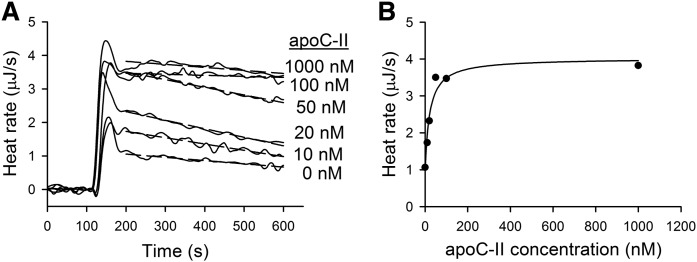
Fig. 5.
Activation of LPL by apoC-II as studied by ITC. A: Raw ITC thermograms of hydrolysis of Intralipid by LPL in the absence or presence of apoC-II. The substrate mixture composition in the ITC cell was as follows: Intralipid corresponding to 1 mg triglyceride/ml, 10 mg/ml BSA, 10 IU/ml heparin, 0.15 M NaCl, and 10 mM TRIS (pH 7.4). Single injections of LPL were made in experiments that contained or did not contain human apoC-II. The concentration of LPL was 1.2 nM in all experiments. B: Hydrolysis heat rate as a function of apoC-II concentration. Heat rate points at 200 s were obtained from (A). The data were fitted using the following equation: v = kcat · L · [(β · C + Kd)/(C + Kd)], where v is the reaction rate, kcat is catalytic rate constant, L is the concentration of LPL, C is the concentration of apoC-II, β is the activation factor that indicates how much more active the LPL/apoC-II complex is compared with LPL alone, and Kd is the equilibrium dissociation constantQ11 (29).