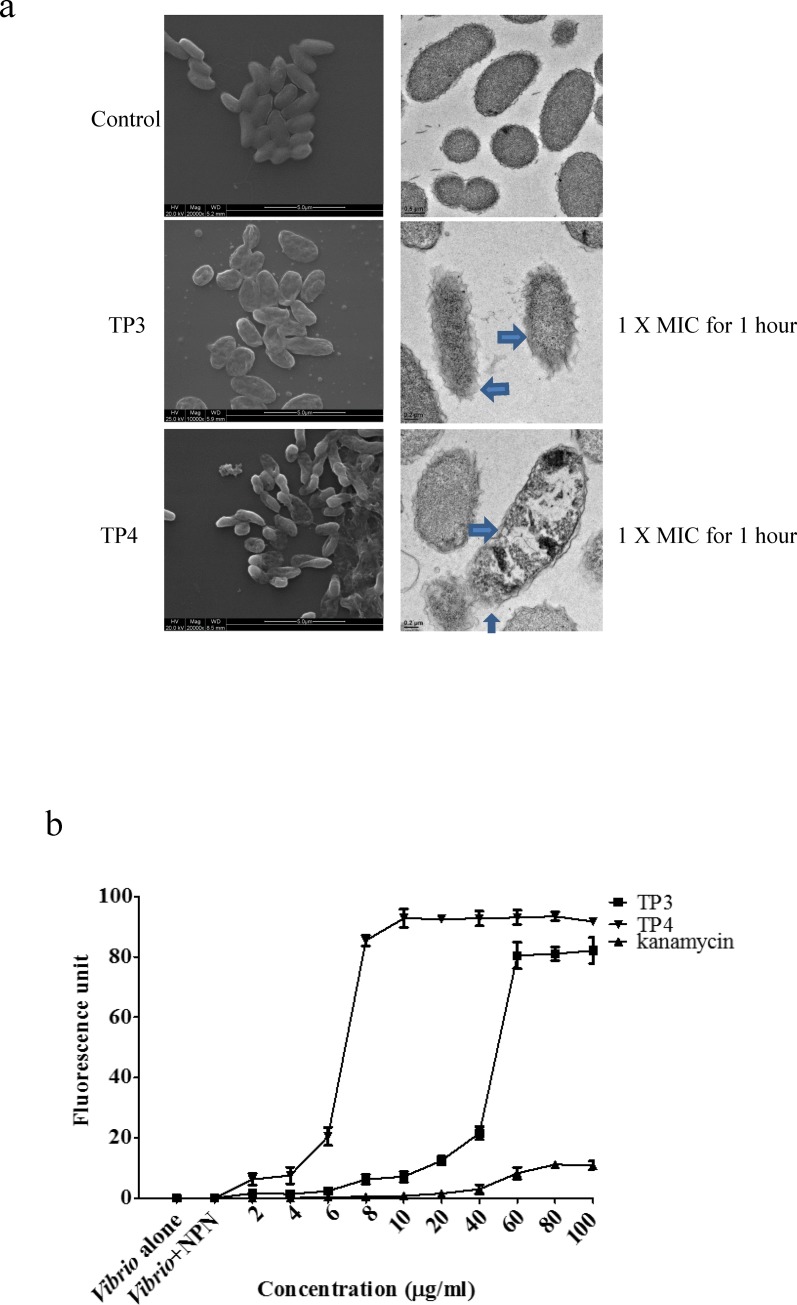
Fig 2. TP3 and TP4 induce membrane permeation and cause membrane disruption in V. vulnificus.
(a) Treatment with TP3 or TP4 resulted in the appearance of cell injuries in V. vulnificus and the formation of electron-dense structures on the surfaces of the cells. The blue arrow indicates damage to the plasma membranes of V. vulnificus cells. The results of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) are shown on the left, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) results are shown on the right. (b) We determined V. vulnificus membrane permeability by measuring the fluorescence resulting from the uptake of 1-N-phenyl-naphthylamine (NPN). We used cultures of V. vulnificus cells alone or V. vulnificus incubated with NPN as the control groups. Cells were treated with TP3, TP4, or kanamycin at different concentrations, and the resulting NPN fluorescence intensities were recorded to determine their correlations with membrane permeability. The data are shown as the means±SE of three independent experiments.