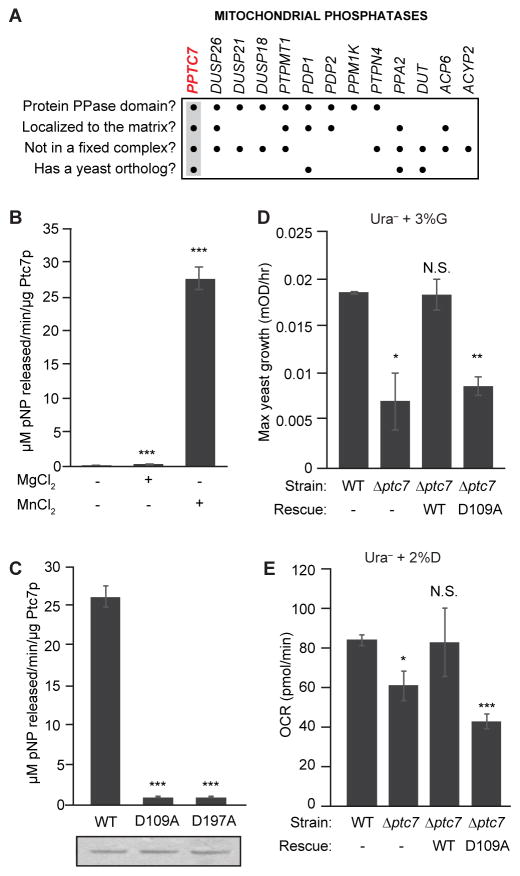
Figure 1. Ptc7p phosphatase activity supports respiratory function.
(A) Summary table of mitochondrial phosphatases, analyzed for protein phosphatase domains, matrix localization, non-association with a protein complex (e.g. PDH), and presence of a yeast ortholog. PPTC7 (highlighted) is the only phosphatase to meet all four criteria.
(B) In vitro phosphatase activity assay of Ptc7p against pNPP with divalent cations Mn2+ and Mg2+ (mean ± SD, n=3).
(C) In vitro pNPP phosphatase activity assay of WT Ptc7p and two mutants predicted to disrupt metal binding (mean ± SD, n=3). Coomassie staining (below) demonstrates comparable protein concentration and purity.
(D) Maximum growth rate of WT and Δptc7 yeast in Ura− media containing 3% glycerol (G) (mean ± SD, n=4). Rescue strains express a plasmid containing ptc7 (WT: wild type ptc7; D109A: catalytically inactive mutant of ptc7).
(E) OCR of same cultures as in (D) grown in Ura− media containing 2% dextrose (D) (mean ± SD, n=3).
* p-value < 0.05; ** p-value < 0.01; *** p-value < 0.001; N.S., not significant.
See also Figure S1.