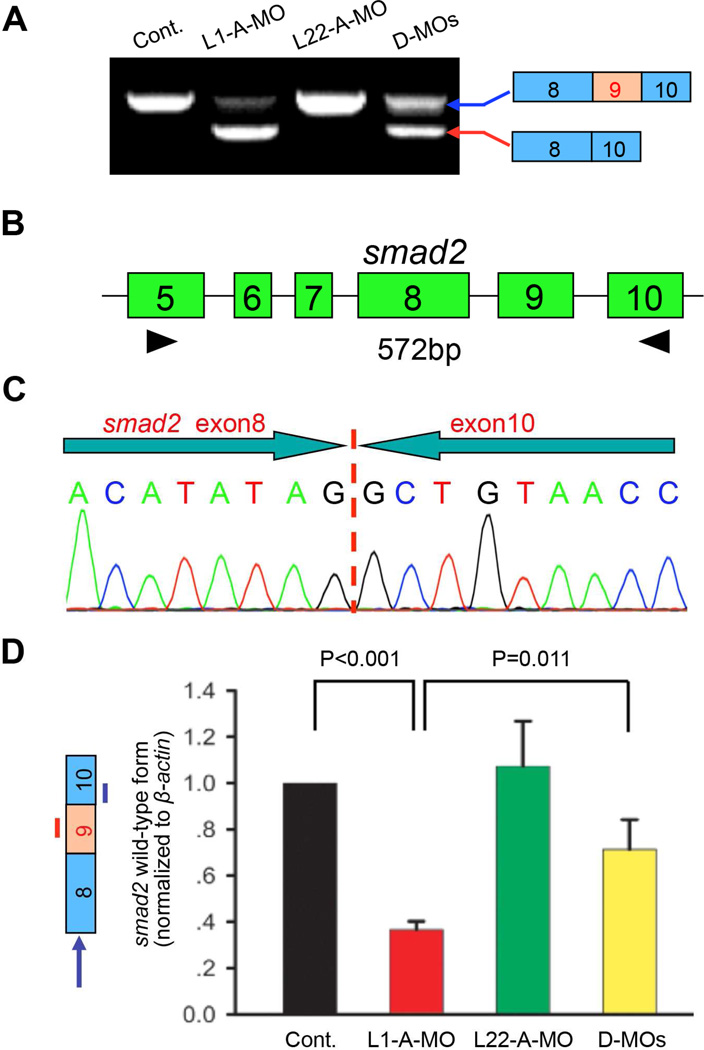
Figure 2. The gastrulation defects in Like1 morphants result from skipping of smad2 exon 9.
(A,B) RT-PCR analysis of smad2 mRNA in Like1, Rpl22 and double morphants (D-MOs). smad2 mRNA was evaluated by RT-PCR using primers (black arrowheads) amplifying the sequences between exons 5 to 10. (C) Like1 knockdown causes skipping of smad2 exon 9. Sequence analysis of the smaller smad2 mRNA species caused by Like1 knockdown (red arrow in panel A). (D) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the relative expression of intact smad2 mRNA (indicated by left panel, blue arrow). The blue and red lines identify the position of real-time primers employed to detect intact smad2 mRNA. Triplicate samples were quantified and the mean ± S.D. is depicted graphically. p-values are indicated. All results are representative of at least 3 experiments performed. See also Figure S2.