Fig. 3.
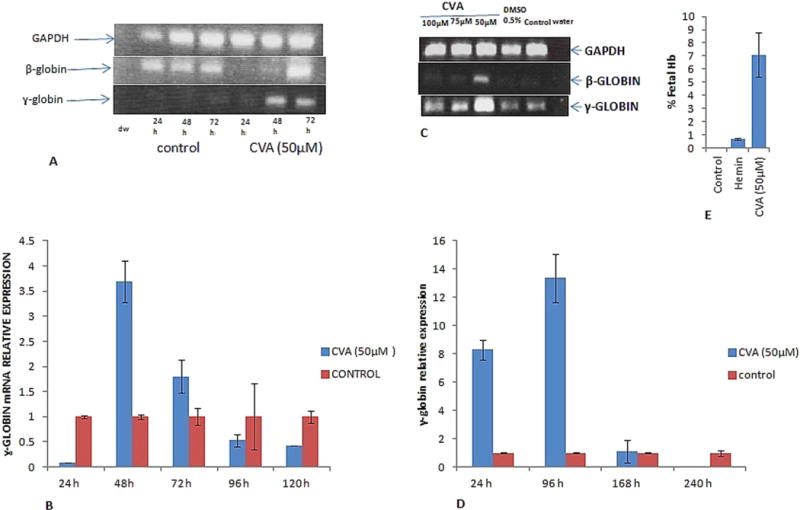
CVA up-regulates γ and β-globin gene expression and fetal hemoglobin synthesis. CVA induced γ-globin gene expression was monitored in A. JK-1 cells using RT-PCR at 24, 48 and 72 h post CVA induction. B. qRT-PCR was used to measure JK-1 cell relative γ-globin gene expression 24, 48, 72, 96 and 120 h post CVA induction. Expression data was normalized to JK-1 GAPDH expression. C. Concentration dependent effect of CVA on JK-1 cell γ-globin gene expression was assayed using semi-quantitative RT-PCR. D. Effect of CVA induction on transgenic mice bone marrow erythroid progenitor stem cells γ-globin gene expression. Relative γ-globin gene expression was assessed using qRT-PCR at 24, 96, 168 and 240 h post CVA induction. γ-globin gene expression was normalized to transgenic mice bone marrow progenitor stem cells GAPDH gene expression. E. effect of CVA on JK-1 cells fetal hemoglobin synthesis. Fetal hemoglobin was assayed in JK-1 cell lysates using alkaline denaturation assay as previously described (Fibach et al., 1993). Hemin was used as a positive control inducer. The experiment was carried out in duplicate, and although precise globin mRNA levels appeared to fluctuate from culture to culture, but relative γ-globin levels were always higher in cells induced in transgenic mice primary bone marrow progenitor stem cells induced with 50 μM CVA. The data represents the mean and corresponding S.D. of three independent experiments. ANOVA was used to analyse the differences between groups and differences were considered significant at P<0.05.
