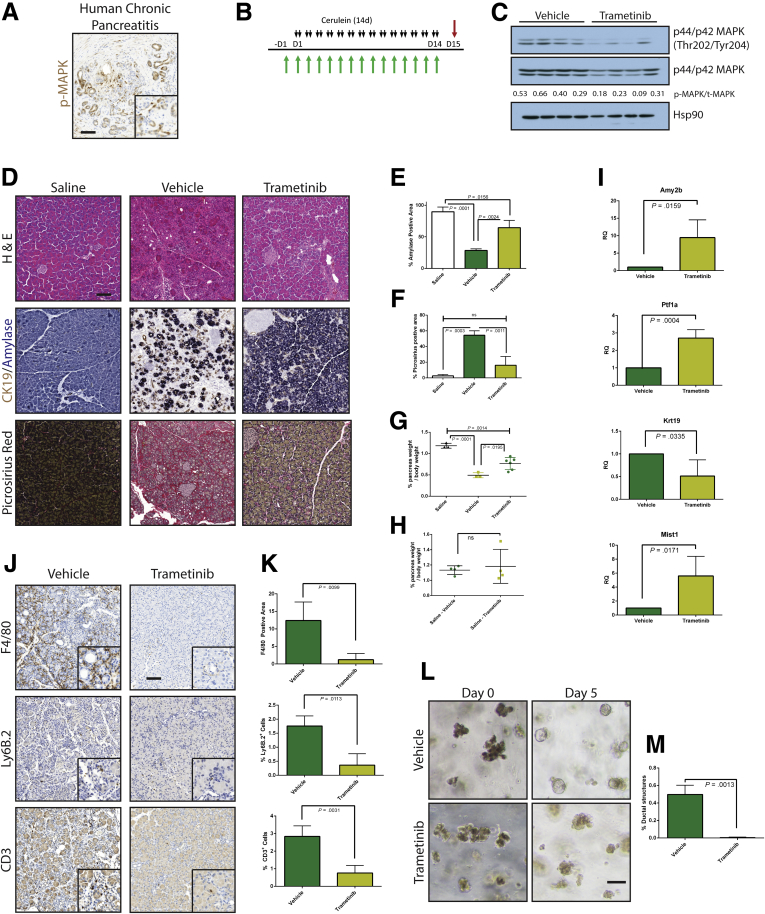
Figure 1.
MEK inhibition can block the onset of CP. (A) Immunohistochemistry for phosphorylated MAPK in human pancreatitis samples. (B) CP protocol with drug pretreatment. Black arrows indicate cerulein injection; green arrows indicate vehicle or trametinib treatment. (C) Immunoblot for levels of phosphorylated MAPK, total MAPK, and the loading control HSP90. The ratio of the band intensities of phosphorylated/total MAPK is indicated under each lane. (D) Histologic characterization of tissue remodeling, hematoxylin-eosin staining (H&E), dual immunohistochemistry with ductal marker CK19 (brown) and acinar marker amylase (blue), and picrosirius red stain, with respective quantitation (E and F) n ≥ 3 for all groups. White indicates saline treated; green indicates vehicle + cerulein; yellow indicates trametinib + cerulein. (G) Relative pancreas mass, defined by percentage pancreas weight over body weight, n = 3 for saline and vehicle, n = 6 for trametinib. (H) Relative pancreas mass, defined by percentage pancreas weight over body weight, n = 4 for all groups. (I) qRT-PCR analysis of acinar markers Amy2b, Ptf1a, and Mist1 and ductal marker Krt19. (J) Immunohistochemistry for macrophages (F/480), neutrophils (Ly6B.2), and T-cells (CD3) with respective quantitation (K) n ≥ 3 for all groups. (L) Acinar cell explants embedded in Matrigel were imaged at Day 0 and Day 5. (M) Acinar to ductal cyst conversion on day 5 was quantitated by a blinded observer, n = 3. Scale bars = 100 μm for all panels, 50 μm for insets. Error bars represent mean with standard deviation.