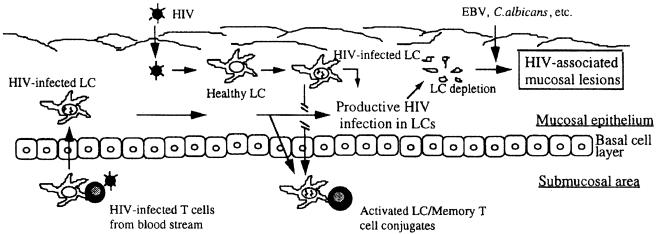
FIG. 1.
Hypothetical model of the role of mucosal Langerhans' cells (LC) in HIV infection. Oral mucosal Langerhans' cells serve as an initial target for HIV infection. The cytopathic changes of Langerhans' cells with a productive HIV infection contribute to selective depletion of Langerhans' cells, which may impair mucosal immunologic protection against colonization by microorganisms causing HIV-associated oral mucosal lesions. Reprinted from reference 81 with permission of the publisher.