Abstract
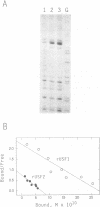
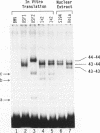
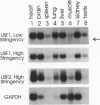
USF is a helix-loop-helix transcription factor that, like Myc, recognizes the DNA binding motif CACGTG. Two different forms of USF, characterized by apparent molecular weights of 43,000 and 44,000, were originally identified in HeLa cells by biochemical analysis. Clones for the 43-kDa USF were first characterized, but only partial clones for the human 44-kDa USF (USF2, or FIP) have been reported. Here we describe a complete cDNA for the 44-kDa USF from murine cells. Analysis of this clone has revealed that the various USF family members are quite divergent in their N-terminal amino acid sequences, while a high degree of conservation characterizes their dimerization and DNA-binding domains. Interestingly, the 3' noncoding region of the 44-kDa USF cDNAs displayed an unusual degree of conservation between human and mouse. In vitro transcription/translation experiments indicated a possible role for this region in translation regulation. Alternative splicing forms of the 44-kDa USF messages exist in both mouse and human. Examination of the tissue and cell-type distribution of USF by Northern blot and gel retardation assays revealed that while expression of both the 43- and 44-kDa USF species is ubiquitous, different ratios of USF homo- and heterodimers are found in different cells.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayer D. E., Kretzner L., Eisenman R. N. Mad: a heterodimeric partner for Max that antagonizes Myc transcriptional activity. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90661-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann H., Su L. K., Kadesch T. TFE3: a helix-loop-helix protein that activates transcription through the immunoglobulin enhancer muE3 motif. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):167–179. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Rutter W. J. Interaction cloning: identification of a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that interacts with c-Fos. Science. 1992 May 15;256(5059):1014–1018. doi: 10.1126/science.1589769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bungert J., Kober I., Düring F., Seifart K. H. Transcription factor eUSF is an essential component of isolated transcription complexes on the duck histone H5 gene and it mediates the interaction of TFIID with a TATA-deficient promoter. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 20;223(4):885–898. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90250-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr C. S., Sharp P. A. A helix-loop-helix protein related to the immunoglobulin E box-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4384–4388. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. The major late transcription factor binds to and activates the mouse metallothionein I promoter. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):973–980. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. S., Shi Y., Shenk T. Adeno-associated virus P5 promoter contains an adenovirus E1A-inducible element and a binding site for the major late transcription factor. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3479–3488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3479-3488.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Morgan J. G., Crabtree G. R., Sharp P. A. The adenovirus major late transcription factor activates the rat gamma-fibrinogen promoter. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):684–688. doi: 10.1126/science.3672119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Schibler U. A liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein, LAP, and a transcriptional inhibitory protein, LIP, are translated from the same mRNA. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):569–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duret L., Dorkeld F., Gautier C. Strong conservation of non-coding sequences during vertebrates evolution: potential involvement in post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 25;21(10):2315–2322. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves R. F., O'Hare P. Sequence, function, and regulation of the Vmw65 gene of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6705–6713. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6705-6713.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P. D., Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. The adenovirus major late transcription factor USF is a member of the helix-loop-helix group of regulatory proteins and binds to DNA as a dimer. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1730–1740. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Kandil A. N. Determination of the c-MYC DNA-binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6162–6166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaulen H., Pognonec P., Gregor P. D., Roeder R. G. The Xenopus B1 factor is closely related to the mammalian activator USF and is implicated in the developmental regulation of TFIIIA gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):412–424. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschbaum B. J., Pognonec P., Roeder R. G. Definition of the transcriptional activation domain of recombinant 43-kilodalton USF. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5094–5101. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski M. T., Gan L., Venuti J. M., Sawadogo M., Klein W. H. Sea urchin USF: a helix-loop-helix protein active in embryonic ectoderm cells. Dev Biol. 1991 Dec;148(2):625–630. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90280-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaigre F. P., Courtois S. J., Lafontaine D. A., Rousseau G. G. Evidence that the upstream stimulatory factor and the Sp1 transcription factor bind in vitro to the promoter of the human-growth-hormone gene. Eur J Biochem. 1989 May 15;181(3):555–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14760.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennard A. C., Egly J. M. The bidirectional upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter binds a single monomeric molecule of the upstream factor. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3027–3034. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto N. G., Moncollin V., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Specific interaction between a transcription factor and the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3563–3570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04118.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J. J., Cheneval D., Dang C. V., Resar L. M., Mezey E., Yang V. W. The upstream stimulatory factor binds to and activates the promoter of the rat class I alcohol dehydrogenase gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15457–15463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Lawe D., Ziff E. B. Association of Myn, the murine homolog of max, with c-Myc stimulates methylation-sensitive DNA binding and ras cotransformation. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):395–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90457-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B. Methylation-sensitive sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc basic region. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):186–189. doi: 10.1126/science.1987636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Rotter V. The helix-loop-helix containing transcription factor USF binds to and transactivates the promoter of the p53 tumor suppressor gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 25;21(2):345–350. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccio A., Pedone P. V., Lund L. R., Olesen T., Olsen H. S., Andreasen P. A. Transforming growth factor beta 1-responsive element: closely associated binding sites for USF and CCAAT-binding transcription factor-nuclear factor I in the type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1846–1855. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Ishizawa S., Yoshida T., Shibahara S. Interaction of upstream stimulatory factor with the human heme oxygenase gene promoter. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Mar 10;188(2):231–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M. Multiple forms of the human gene-specific transcription factor USF. II. DNA binding properties and transcriptional activity of the purified HeLa USF. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11994–12001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Van Dyke M. W., Gregor P. D., Roeder R. G. Multiple forms of the human gene-specific transcription factor USF. I. Complete purification and identification of USF from HeLa cell nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11985–11993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotto K. W., Kaulen H., Roeder R. G. Positive and negative regulation of the gene for transcription factor IIIA in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):651–662. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirito M., Walker S., Lin Q., Kozlowski M. T., Klein W. H., Sawadogo M. Members of the USF family of helix-loop-helix proteins bind DNA as homo- as well as heterodimers. Gene Expr. 1992;2(3):231–240. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga K., Nakamura Y., Sakata K., Fujimori K., Ohkubo M., Sawada K., Sakiyama S. Enhanced expression of a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene in human lung cancers. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 1;47(21):5616–5619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Sirito M., Sawadogo M. Single-step purification of bacterially expressed polypeptides containing an oligo-histidine domain. Gene. 1992 Feb 1;111(1):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90608-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zervos A. S., Gyuris J., Brent R. Mxi1, a protein that specifically interacts with Max to bind Myc-Max recognition sites. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90662-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman K., Alt F. W. Expression and function of myc family genes. Crit Rev Oncog. 1990;2(1):75–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwartkruis F., Hoeijmakers T., Deschamps J., Meijlink F. Characterization of the murine Hox-2.3 promoter: involvement of the transcription factor USF (MLTF). Mech Dev. 1991 Mar;33(3):179–190. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]