Figure 2.
An LTMR-RZ Genetic Toolkit and Contributions of LTMR-RZ Interneurons to Tactile Perception
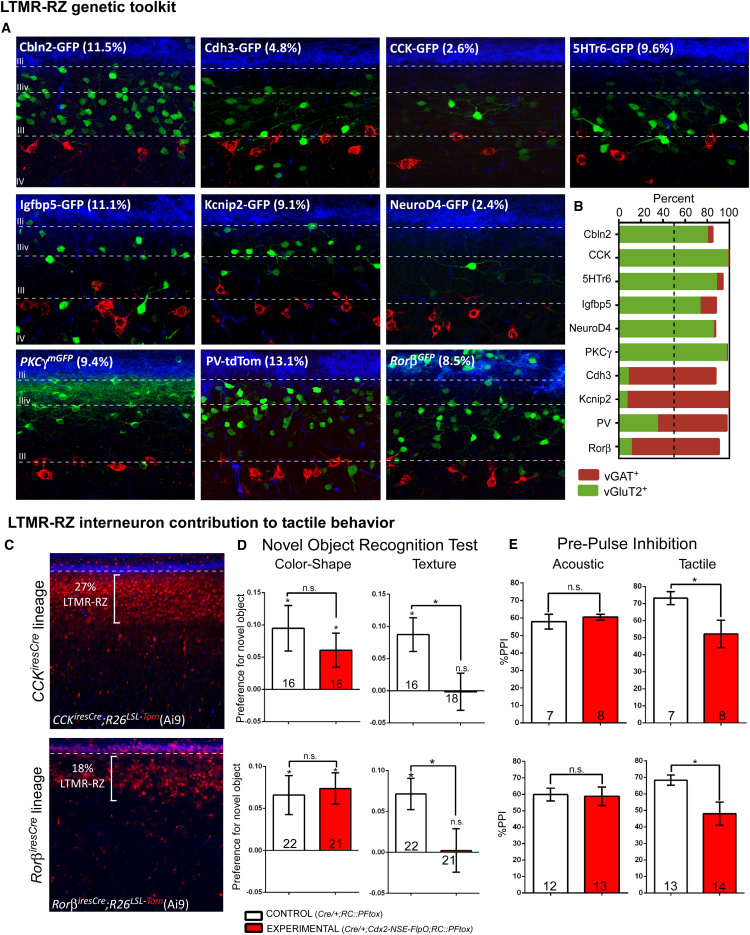
(A) Sagittal sections of the LTMR-RZ from the interneuron GFP/Tomato mouse lines. Fluorescent reporters are in green, CTB-labeled PSDCs are in red, IB4 binding is in blue. Percentage of the LTMR-RZ is in parentheses.
(B) Neurotransmitter quantification for the ten interneuron lines. Excitatory and inhibitory neurons labeled with vGluT2iresCre and vGATiresCre mouse lines, respectively.
(C) Sagittal spinal cord section from a CCKiresCre;R26LSL-tdTom(Ai9) mouse and an RorβiresCre;R26LSL-TdTom(Ai9) mouse. IB4 lamina IIi in blue.
(D) Discrimination indices for color-shape NORT (left) and texture NORT (right). CCKiresCre;Cdx2-NSE-FlpO;RC::PFTox animals (top), RorβiresCre;Cdx2-NSE-FlpO;RC::PFTox animals (bottom). Positive value indicates preference for the novel object compared to the familiar object. Values displayed as percentages. ∗p < 0.05.
(E) Percentage of inhibition of startle response to 125 dB noise in control and mutant littermates when the startle noise is preceded by an 80dB acoustic prepulse (left) or a light air puff of 1.5 PSI (right). CCKiresCre;Cdx2-NSE-FlpO; RC::PFTox animals (top), RorβiresCre;Cdx2-NSE-FlpO;RC::PFTox animals (bottom). ∗p < 0.05.
For further details and statistical methods used, see STAR Methods. See also Figures S2 and S3; Table S1.