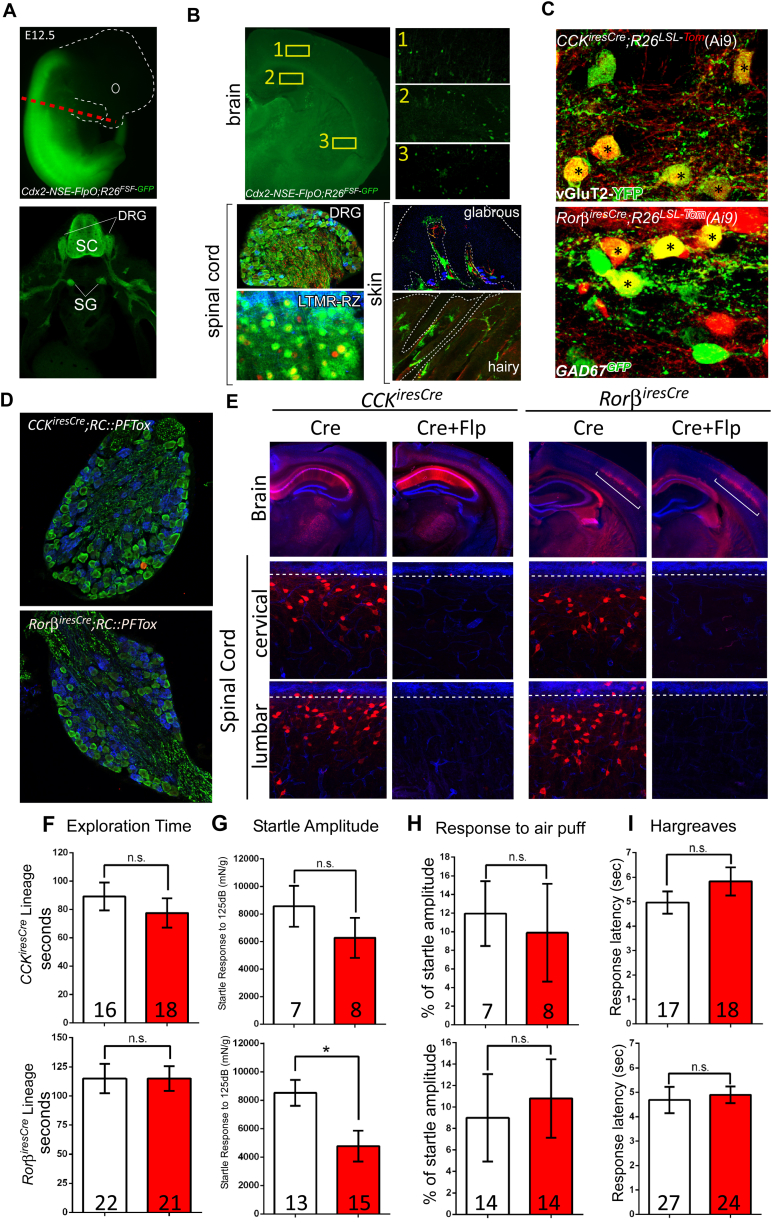
Figure S3.
Characterization of Intersectional Inactivation and Additional Behavioral Assays, Related to Figure 2
(A) Cdx2-NSE-FlpO;R26FSF-GFP E12.5 embryo depicting caudal expression of FlpO (top). Cross section at red dotted line (bottom). Early in development Cdx2-NSE-FlpO recombination is restricted to posterior neural plate, prospective spinal cord territory. See STAR Methods and (Coutaud and Pilon 2013). Note specific FlpO expression in caudal neuronal tissues (spinal cord, SC; dorsal root ganglia, DRG; sympathetic ganglia, SG) but not in brain, internal organs or skin.
(B) Adult characterization of brain, spinal cord, and skin tissue from a Cdx2-NSE-FlpO; R26FSF-GFP animal. Adult brain characterization reveals very sparse FlpO activity in the brain (top). Yellow insets show very low levels of recombination in the cortex (1), hippocampus (2), and striatum (3). Adult DRG and spinal tissue show near complete FlpO recombination (bottom left, IB4 binding in blue). Adult glabrous and hairy skin sections (bottom right) show no FlpO activity in skin cells (outlined in white dotted lines) including Troma1+ merkel cells depicted in blue for the glabrous skin inset. Neurofilament 200 staining in red, GFP staining in green.
(C) Neurotransmitter characterization of CCKiresCre and RorβiresCre lineages in the LTMR-RZ. Asterisk denotes overlap.
(D) DRG cross-sections from CCKiresCre;RC::PFtox (top) and RorβiresCre;RC::PFtox (bottom) animals. Cre recombination of RC::PFtox results in mCherry expression, depicted in red. Note very minimal DRG Cre recombination of CCKiresCre (top) and no DRG Cre recombination of RorβiresCre (bottom). IB4 binding in blue, Neurofilament-200 staining in green.
(E) Cross-sections through brain and cervical/lumbar spinal cords from CCKiresCre;RC::PFtox, CCKiresCre;Cdx2-NSE-FlpO;RC::PFtox, RorβiresCre;RC::PFtox and RorβiresCre;Cdx2-NSE-FlpO;RC::PFtox animals (left to right). Cre recombination of RC::PFtox results in mCherry expression in brain and spinal cord, depicted in red. Combined Cre and Flp recombination from Cdx2-NSE-FlpO of RC::PFtox results in loss of mCherry expression and expression of Tetanus Toxin specifically in spinal cord but not in the brain. For brain sections NeuN is depicted in blue, for spinal cord sections IB4 binding is depicted in blue.
(F–H) Additional behavior assays CCKiresCre;Cdx2-NSE-FlpO;RC::PFtox (top panels), RorβiresCre;Cdx2-NSE-FlpO;RC:;PFtox (bottom panels). (F) Exploration time during texture NORT. (G) Startle amplitude to 125dB noise during PPI test. RorβiresCre;Cdx2-NSE-FlpO;RC::PFtox mutant animals display a much lower startle response than control littermates, indicating some motor deficits (∗p < 0.05). (H) Response to a light air puff stimulus alone. Responses are expressed as a percent of startle response to a 125-dB noise.
(I) Hargreaves temperature sensitivity assay.