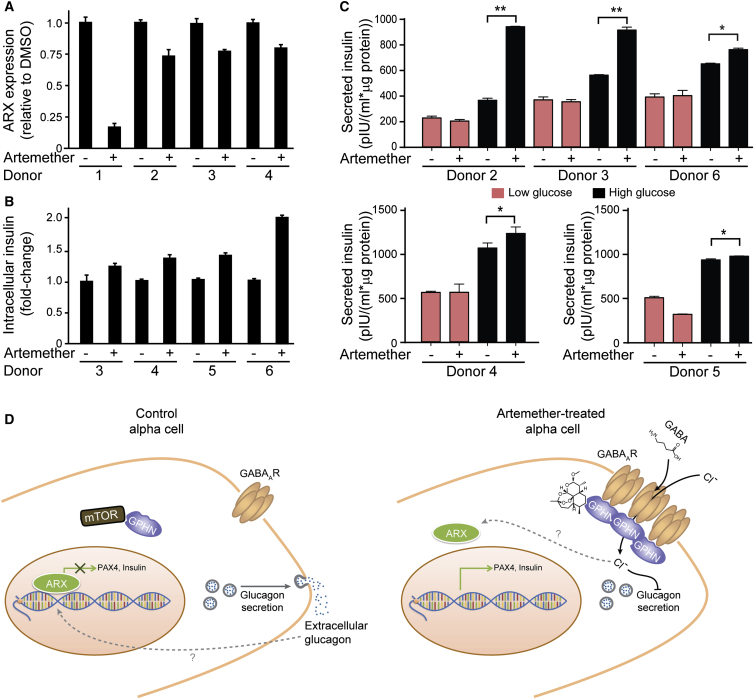
Figure 7.
Artemether Enhances Insulin Secretion in Human Islets
(A) RT-qPCR assay for ARX expression in human islets treated with control DMSO or 10 μM artemether for 72 hr. Error bars represent mean ± SD.
(B) Measurement of intracellular insulin content in human islets treated with control DMSO or 10 μM artemether for 72 hr. Error bars represent mean ± SD.
(C) Measurement of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in human islets treated with control DMSO or 10 μM artemether for 72 hr (two replicates each donor; ∗∗p < 0.005; ∗p ≤ 0.05). Error bars represent mean ± SD.
(D) Proposed mechanism of action of artemether. By stabilizing gephyrin, artemether increases GABA-receptor signaling in α cells, thereby preventing glucagon secretion. Decreased extracellular glucagon concentration induces loss of α cell identity and increase of insulin expression.
See also Figure S6.