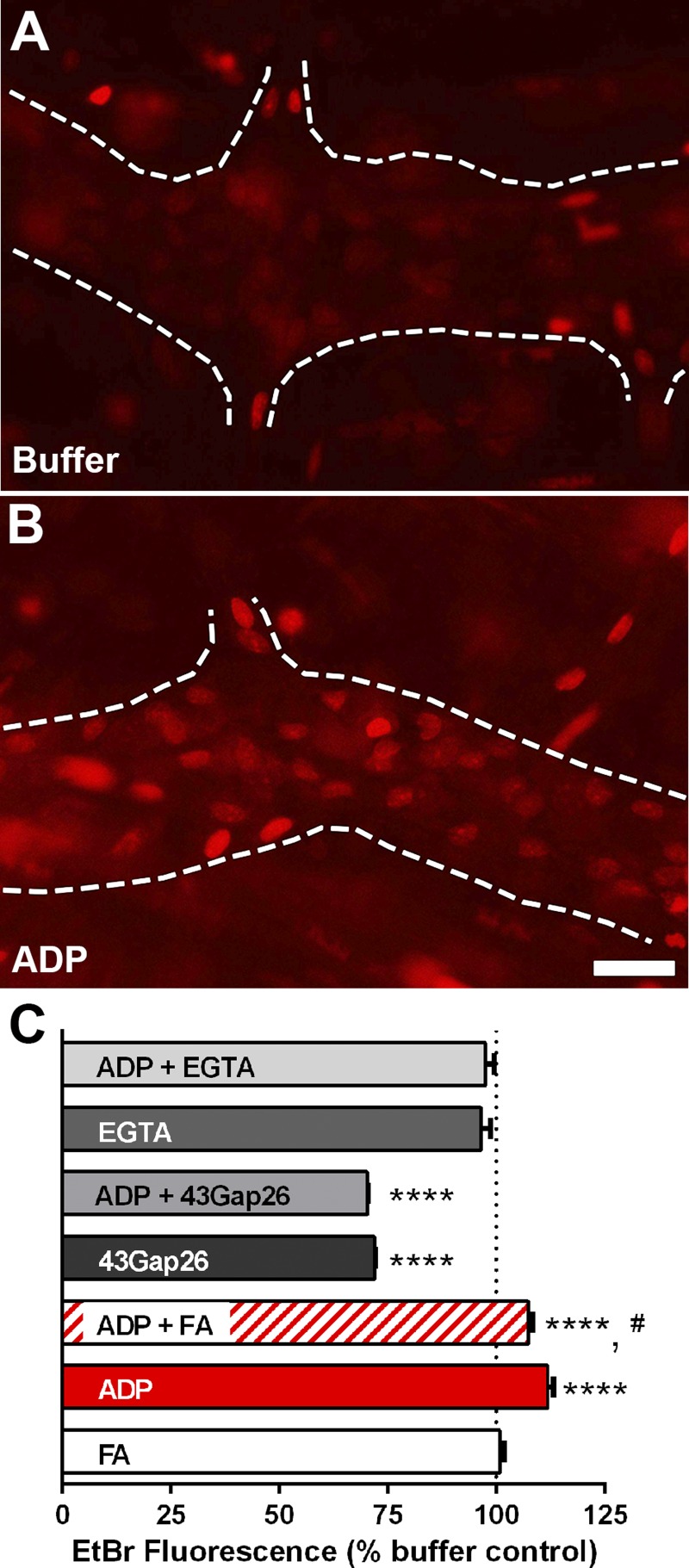
Fig. 4.
The effect of fluoroacetate (FA) on hemichannel-dependent dye uptake by myenteric glia in the mouse colon. A and B: representative epifluorescence images showing ethidium bromide (EtBr) fluorescence in whole-mount preparations of the myenteric plexus from the mouse colon exposed to buffer (A) or ADP (B). Glial cells within myenteric ganglia (outlined by dashed lines) normally display a low amount of dye uptake (A) that increases robustly when stimulated with ADP (B). C: quantification of the effects of FA, the connexin-43 mimetic peptide 43Gap26, the Ca2+ chelator EGTA, and ADP on mean glial cell EtBr fluorescence in whole-mount preparations of the mouse myenteric plexus. Scale bar (B) = 10 μm and applies to A and B. Measurements are representative of n = 225 glia to 373 glial cells from at least 3 mice. ****P < 0.0001 compared with buffer, #P < 0.05 compared with ADP, ANOVA.