Table 1.
Categories of DNA damage.
| DNA damage category | Structures and names | Agents | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| N2-alkylG |
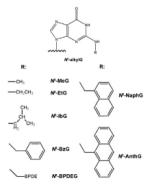
|
Alkylation agents: Formaldehyde, Ethanol, Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, et al. |
[13,14,16,17] |
| N2,N2-dialkylG |
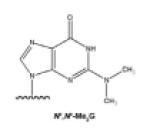
|
Alkylation agents: Formaldehyde |
[16] |
| N6-alkylA |
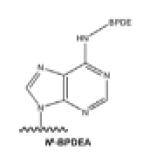
|
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P), et al. |
[20] |
| O6-alkylG |
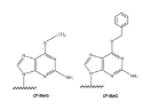
|
Alkylation agents | [18,19] |
| Oxidized lesion |
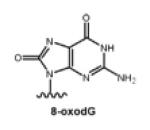
|
Oxidation agents, ionizing radiation, UV irradiation, et al. |
[25,26] |
| Etheno (ε) DNA adducts |
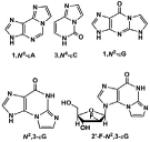
|
Bioactivated Vinyl monomers: mutagens vinyl chloride, vinyl carbamate, et al. |
[20,21] |
| DNA-DNA or DNA-protein cross-links |
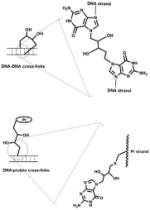
|
Bis- electrophilic agents: 1,3-butadiene, et al. |
[22–24] |
| Arylation adducts |
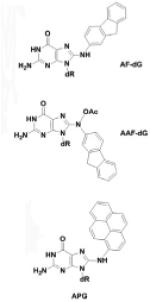
|
Arylamines and N-acetyl arylamines, 1-Nitropyrene, et al. |
[27,28] |
| DNA-DNA coordinated cross-links |
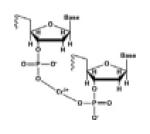
|
Heavy metal ions: Cr (III) ion |
[29] |
| Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer (CPD) photoproduct |
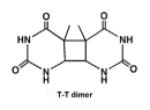
|
UV radiation, et al. |
[30,31] |
| Apurinic/ apyrimidinic (AP) sites |
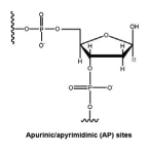
|
Spontaneous, chemically- induced, enzyme- catalyzed hydrolysis of the N-glycosyl bond |
[32] |
