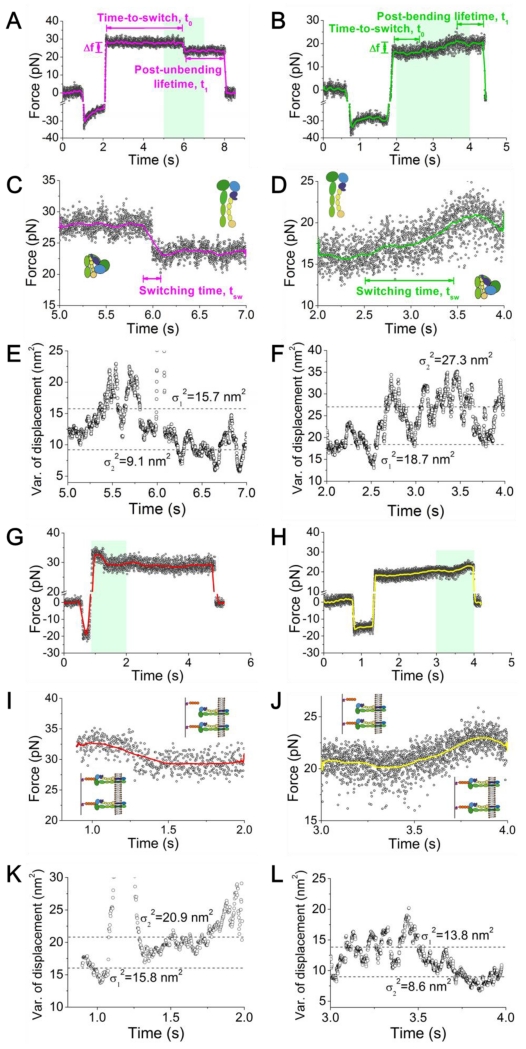
Figure 2.
BFP force signals of position-clamp αVβ3 unbending (A,C,E) and bending (B,D,F) conformational change events, and breakage (G,I,K) and formation (H,J,L) of an addition bond. (A-D) Representative force vs. time data showing a putative integrin unbending (A, C), and bending (B, D) event. A higher force resolution was obtained by smoothing the raw data using the Savitzky-Golay method (curves). Force changes (Δf), switching time (tsw±), and time-to-switch (t0±) are indicated. (A,B) The overall signals of BFP cycles that contain an integrin unbending (A) or bending (B) event. (C,D) The zoom-in views of the BFP signals within the cyan-shaded time windows indicated in panel (A) or (B), which include the conformational changes of interest. The putative integrin global conformations were depicted by the cartoons before and after the said changes. (E,F) 100-point sliding variance of the displacement in (C) and (D) versus time. A decrease (E) or increase (F) in the thermal fluctuation (from σ12 to σ22, dashed lines) followed integrin unbending or bending, indicating the stiffening or softening of the integrin molecule, respectively. (G-J) Representative force vs. time data showing the dissociation of a bond from a two-bond adhesion (G, I) and formation (H, J) of an additional bond. A higher force resolution was obtained by smoothing the raw data using the Savitzky-Golay method (curves). (G,H) The overall signals of BFP cycles that contain an additional bond dissociation (G) or formation (H) event. (I,J) The zoom-in views of the BFP signals within the cyan-shaded time windows indicated in panel (G) or (H), which include the additional bond dissociation or formation. (K,L) 100-point sliding variance of the displacement in (I) and (J) versus time. An increase (K) or decrease (L) in the thermal fluctuation (from σ12 to σ22, dashed lines) followed bond dissociation or formation, indicating the weakening or strengthening of the linkage between the two surfaces, respectively.