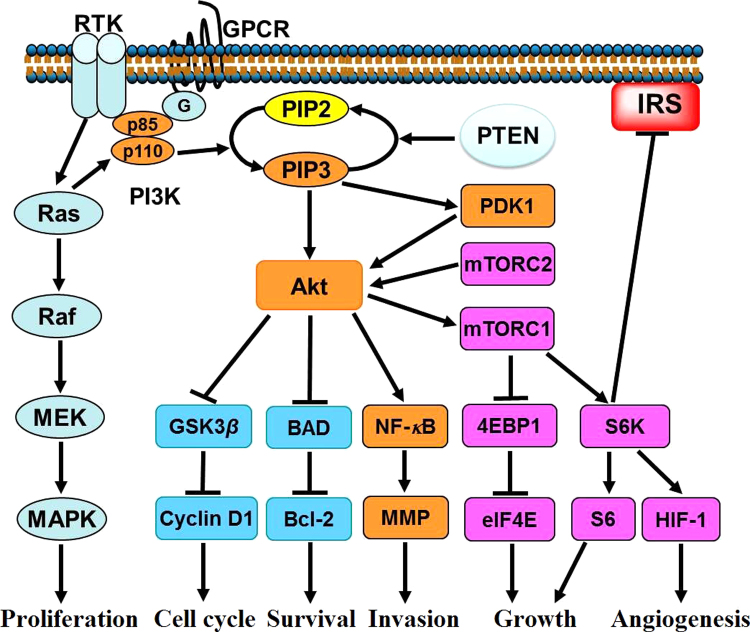
Figure 2.
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway involved in tumorigenesis and metastasis. After activation by RTKs, GPCR or RAS, PI3K catalyzes the phosphorylation of PIP2 to generate PIP3, which binds and recruits Akt and PDK1. Akt can be activated by PDK1 and mTORC2, after recruitment by PIP3. By increasing the level of cyclin D1, Akt promotes the cell cycle progression. Akt also acts to maintain cell survival by phosphorylation of BAD and release of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. Furthermore, Akt regulates cell growth by phosphorylation of the downstream mTORC1, which promotes translation of mRNAs to synthesize protein via p70S6K-S6 and 4E-BP1-eIF4E pathways. In addition, HIF-1α is up-regulated downstream of mTORC1, leading to angiogenesis. By activating NF-κB and inducing secretion of MMP, Akt promotes cell invasion. However, the mTORC1/S6K cascade negatively regulates IRS, which leads to a feedback loop. 4E-BP1, 4E-binding protein 1; GPCR, G protein-coupled receptor; GSK3β, glycogen synthesis kinase 3β; HIF-1, hypoxia-inducible factor 1; IRS, insulin receptor substrate; p70S6K, p70S6 kinase; PDK1, 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase.