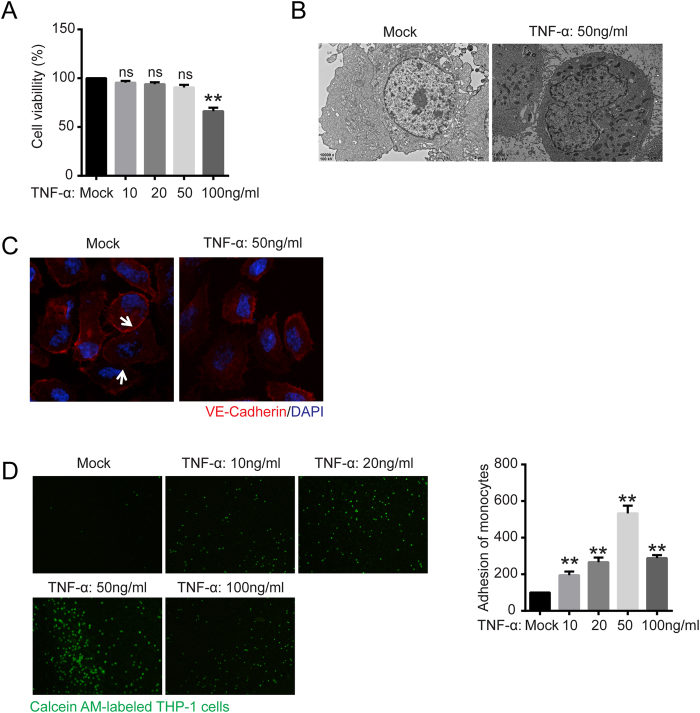
Figure 1. TNF-α impaired vascular epithelial cell tight junctions and increased vascular epithelial cell adhesion.
(A) Cell viability was evaluated with CCK-8 assays. EA.hy926 cells were treated with 0, 10, 50, and 100 ng/ml TNF-α for 24 h and treated with WST-8 for 1 h at 37 °C. The absorbance at 450 nm was then measured with a microplate reader. ns, not significant versus untreated cells. (B) Transmission electron microscopy characterization of EA.hy926 cells with or without TNF-α treatment (50 ng/ml) for 24 h was performed (10000 × magnification). (C) Confocal immunofluorescence analysis of EA.hy926 cells treated with TNF-α using VE-Cadherin rabbit mAb (red) and DAPI (blue). (D) Monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells was quantified via monocyte adhesion assay. Calcein AM-labeled THP-1 cells were incubated with EA.hy926 cells in a 96-well plate for 1 h at 37 °C. The plate was then washed three times with PBS, and the fluorescence was measured. The data are the mean ± SD of three independent assays (**p < 0.01). Mock, EA.hy926 without treatment.