Figure 2.
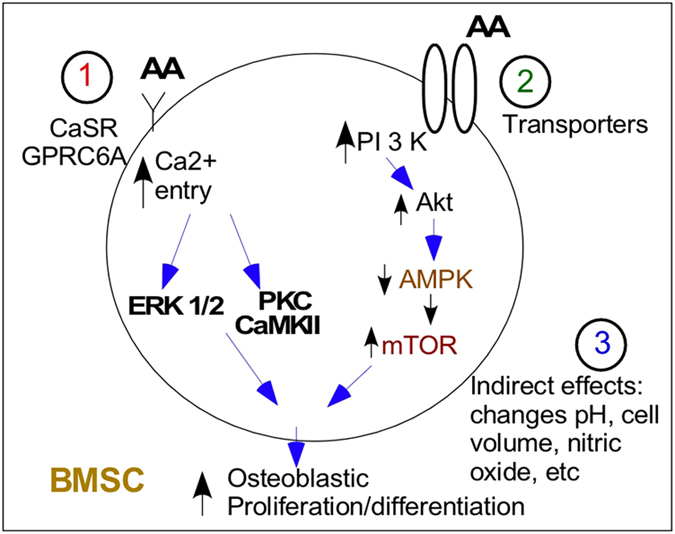
Direct and indirect amino-acid effects on BMSC function. Amino acids can (1) bind to the calcium receptor decrease the threshold for activation of this receptor by calcium or induce calcium oscillations; (2) be taken up directly by a series of cation transporters where they affect energy balance or mitochondrial function; or (3) have indirect effects by increasing production of, for example, nitric oxide (with arginine uptake), induce changes in cell pH or by being exchanged with sodium (sodium/AA transporter) alter cell swelling, cytoskeleton and so on.
