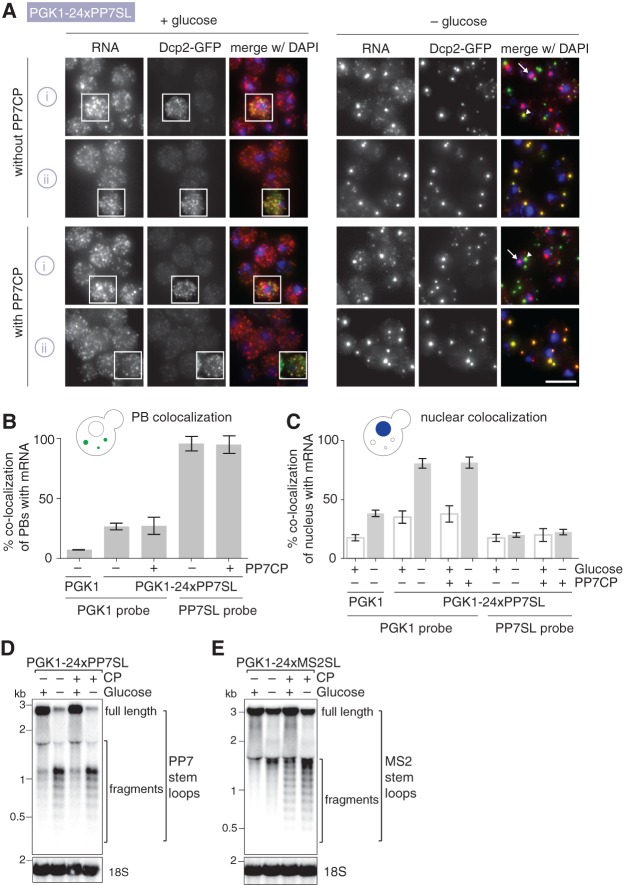
FIGURE 2.
(A) Tagging of PGK1 mRNA at 3′ end with 24xPP7SL alters its cellular localization and causes 3′-end fragments of PP7SL to enrich in PBs. smFISH, imaging and image processing was performed as in Figure 1B using strains expressing DCP2-GFP and either PGK1 or PGK1-24xPP7SL. Fluorescent DNA probes target either the PGK1 (i) or PP7SL (ii) moieties (Supplemental Table S3). White arrows show example cells with large mRNA foci colocalizing with the nucleus. Scale bar, 5 µm. (B) Quantification of colocalization of PBs with mRNA in glucose starvation conditions shown in Figure 2A. Percentage depicts number of PBs colocalizing with mRNAs compared to total number of PBs. n = 3 biological replicates with each >800 counted PBs; bars depict SD. Quantification of colocalization was performed on all planes of a 3D stack image using the Colocalization Threshold tool in Fiji. (C) Quantification of colocalization of nuclear DNA with mRNA foci in glucose-rich and glucose starvation conditions shown in Figure 2A. Percentage depicts nuclear DNA (judged by DAPI signal) colocalizing with mRNAs compared to total number of nuclear DNA. n = 3 biological replicates with each >300 counted nuclei; bars depict SD. Quantification of colocalization was performed on all planes of a 3D stack image using the Colocalization Threshold tool in Fiji. (D,E) Presence of stem–loops causes transcript fragmentation. Cells expressing DCP2-GFP and either PGK1-24xPP7SL or PGK1-24xMS2SL together with or without their respective coat proteins were grown at 25°C to OD600 0.6 to 0.8 in synthetic complete media containing 2% glucose, then shifted to synthetic complete media with or without glucose for 30 min and harvested for total RNA extraction using hot phenol. Ten micrograms of total RNA was separated on a 0.7% formaldehyde agarose gel and transferred to a nylon N+ membrane as described in Farnung et al. (2012). The stem–loops and the 18S RNA are visualized with radioactively end-labeled, sequence-specific oligos (see Supplemental Table S4 for sequences).