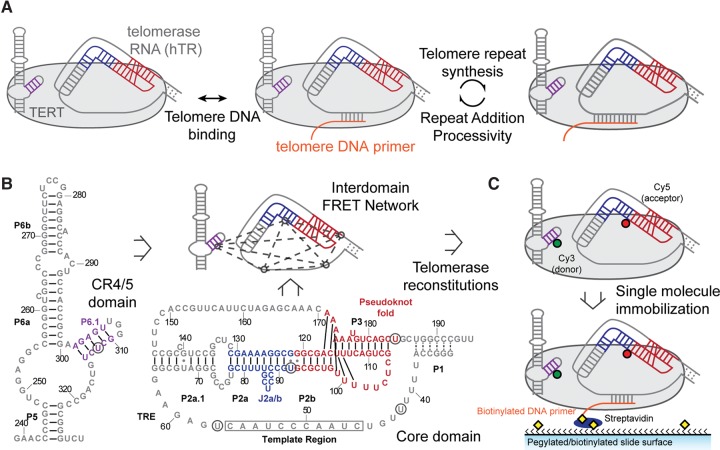
FIGURE 1.
Single-molecule FRET network in the active telomerase RNP. (A) A simplified catalytic mechanism of telomerase is delineated. Telomerase binds to a DNA substrate and reverse transcribes the integral RNA template. The nascent DNA is realigned with the downstream template region, allowing addition of a subsequent telomere repeat to the DNA substrate. (B) Secondary structures of core and CR4/5 domains used in telomerase reconstitution. Five label sites (denoted by black circles) span the two domains and create a network of FRET pairs. Secondary structure information was adapted from the telomerase database (Podlevsky et al. 2008). (C) Dye-labeled RNA fragments are reconstituted with TERT to generate catalytically active RNPs. Each complex is surface immobilized through a 5′ biotinylated DNA primer (TG)6TTAGGG that hybridizes to the template region of telomerase RNA.