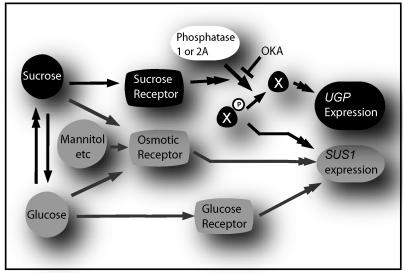
Figure 2.
OKA-sensitive regulation of UGP and SUS1 genes. The boxes and arrows represent hypothetical pathways for Suc, osmoticum, and Glc signaling. Double arrowheads represent multiple or unknown steps. An unknown phosphorylated intermediate (X) antagonistically regulates SUS1 or UGP gene expression depending on phosphorylation status. OKA inhibits PP1 and 2A, and prevents dephosphorylation of X. This probably causes accumulation of X-P and depletion of X, which in turn strongly up-regulates SUS1, and suppresses expression of UGP. The enzymatic interconvertability of Glc and Suc is indicated, both contributing also to osmotic status, similarly to some unmetabolizable compounds (e.g. mannitol). For simplicity, the same PP is indicated as important for the expression of UGP and SUS1; in fact, we cannot exclude that the two genes are regulated by distinct OKA-sensitive PPs.