Figure 3. Effect of P-Rex1 RNAi on the expression of genes regulated by HRG.
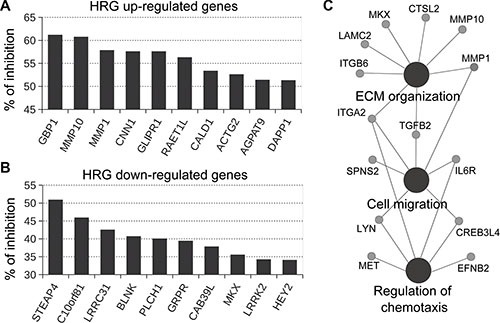
T-47D cells were transfected with two different P-Rex1 RNAi sequences (P-Rex #1 and P-Rex #2), or a non-target control RNAi (NTC). After 16 h, cells were serum starved for 48 h and stimulated with HRG (20 ng/ml) or vehicle for 6 h. Gene expression profiling was carried out using an Affymetrix GeneChip Human Gene 1.0 ST Array. P-Rex1-regulated genes were defined as those in which both P-Rex1 RNAi duplexes (#1 and #2) caused a statistically significant change (p < 0.05) in gene expression compared to NTC and parental cells. (A) Effect of P-Rex1 RNAi on genes induced by HRG. (B) Effect of P-Rex1 RNAi on genes repressed by HRG. For A and B, results are expressed as % of inhibition by P-Rex1 RNAi of the induction (for A) or repression (for B) in gene expression caused by HRG. Only the top 10 P-Rex1 regulated genes are shown. (C) CluePedia network of functionally enriched pathways and genes modulated by the HRG/P-Rex1 pathway in T-47D cells.
