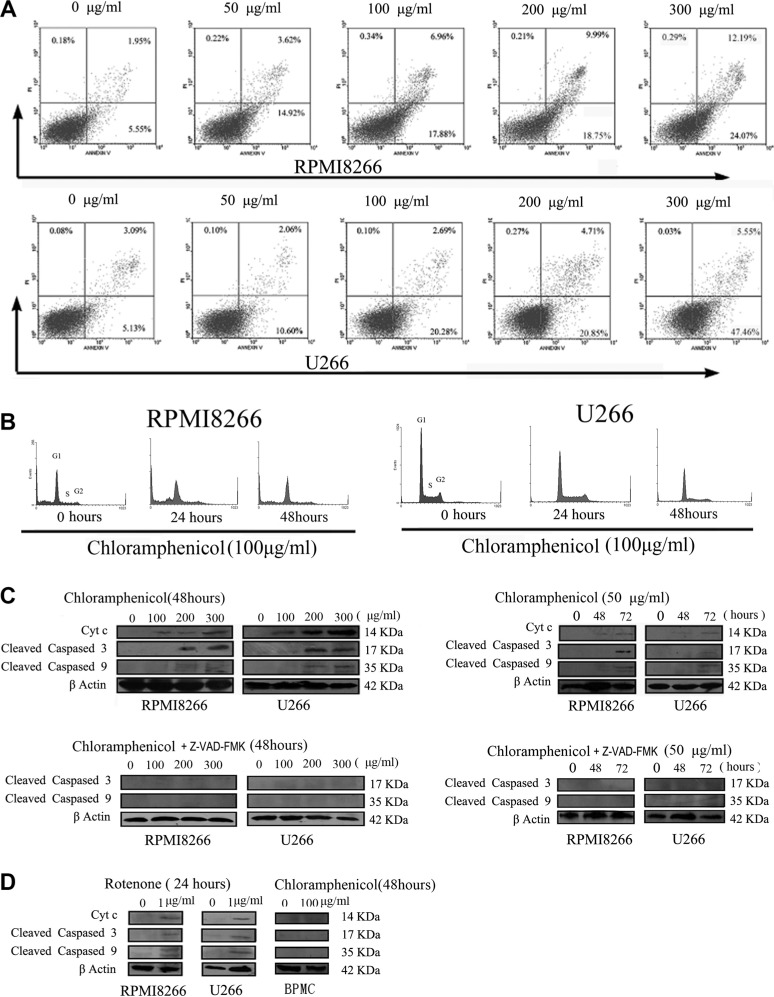
Figure 4. Chloramphenicol-induced apoptosis.
(A) Flow cytometric analysis showed that chloramphenicol dose-dependently increased early (annexin V positive and PI negative cells) and late (annexin V and PI positive cells) apoptosis rates. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of the MM cell cycle during treatment with 100 μg/mL chloramphenicol for 0, 24 and 48 h. The differences were not statistically significant in four separate experiments, P > 0.05. (C) Western blot analysis showing that prolonged treatment with chloramphenicol (≥ 100 μg/mL or 50 μg/mL) increased levels of Cytc, cleaved caspase 9, and cleaved caspase 3 in MM cells (upper). The caspase activation was completely inhibited by 25 μM Z-VAD-FMK (lower). β actin served as a loading control. (D) Like chloramphenicol, rotenone increased levels of Cytc, cleaved caspase 9, and cleaved caspase 3 in MM cells (left and middle). Chloramphenicol (100 μg/mL for 48 h) did not increase Cytc, cleaved caspase 9 or cleaved caspase 3 in PBMCs (right).