Figure 6. Effects of miR-99a/100 on DNA repair processes are regulated by SMARCA5 and SMARCD1.
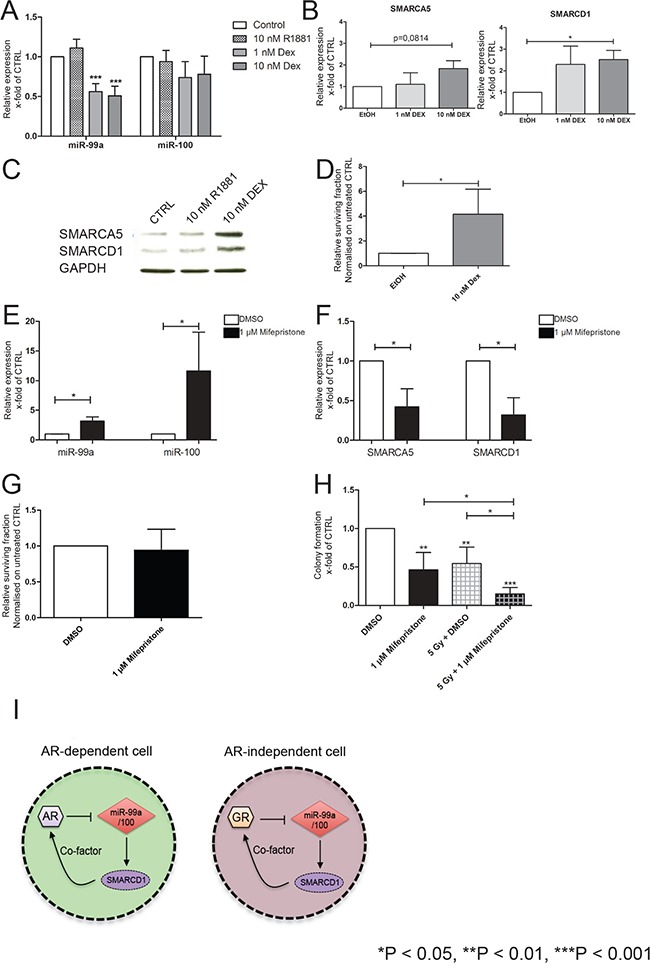
A. qRT-PCR analysis of miR-99a and miR-100 expression in CB cells treated with R1881 or dexamethasone (DEX) for 72 h (n= 5 PCa). B. qRT-PCR analysis of SMARCA5 and SMARCD1 expression in CB cells treated with DEX for 72 h (n= 5 PCa). C. Representative western blot analysis of SMARCA5 and SMARCD1 in CB cells treated with R1881 or DEX for 72 h. D. Cell viability assay after 72 h of CB cells exposed to DEX for 72 h followed by irradiation (Gy 5, n=3 PCa). E. qRT-PCR analysis of miR-99a and miR-100 expression in total primary cell populations treated with Mifepristone for 72 h (n= 5 PCa). F. qRT-PCR analysis of SMARCA5 and SMARCD1 expression in total primary cell populations treated with Mifepristone for 72 h (n= 5 PCa). G. Cell viability assay after 72 h of total primary cell populations after exposure to DEX for 72 h followed by irradiation (Gy 5, n=5 PCa). H. Colony forming efficiency of primary prostate cells after being exposure to Mifepristone for 72 h followed by irradiation (Gy 5, n=5 PCa). I. Schematic representation of the hypothesis, which proposes a feedback loop between androgen receptor (AR)-miR99a/100-SMARCD1 and glucocorticoid receptor (GR)-miR99a/100-SMARCD1 in androgen dependent and androgen independent cells. Data are expressed as mean ± s.d. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (Student's ttest).
