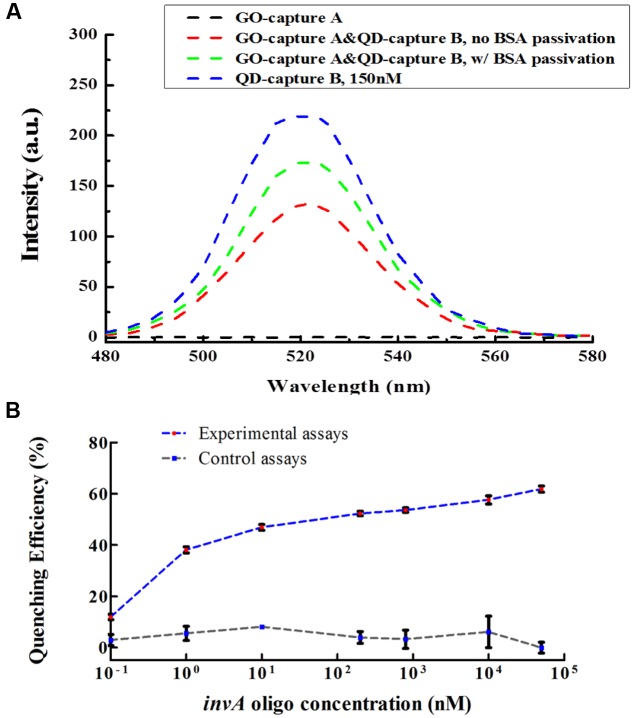
FIGURE 3.
The BSA passivation effect and quenching efficiency of the developed invA gene biosensor. (A) The BSA passivation effect in decreasing the non-specific adsorption between GO and QD conjugates. Briefly, in order to check the BSA passivation effect in preventing unspecific binding between QD and GO conjugates, the GO-capture A conjugate was further treated with or without 0.5 mg/mL BSA at RT for 30 min and then rinsed with DI-H2O, then the fluorescence intensity was measured. The data were analyzed by OriginPro 8.5. (B) For the quenching efficiency assays, in 50 μl reaction volume, BSA passivated GO-capture A (60 μg/mL) was first incubated with serially diluted invA oligo at 55°C for 10 min, then 150 nM QD-capture B was added to the reaction mixture and incubated at 55°C for another 10 min. The fluorescence intensity was measured under 320 nm excitation wavelength and the values at 520 nm were extracted for the calculation of quenching efficiency. The only difference between the experimental assays and the control assays was that the BSA passivated GO-capture A which was included in the experimental assays was replaced by BSA passivated GO (without capture A) in the control assays. The SEM (Standard Error of the Mean) error bars were calculated from at least three replicates. The data were analyzed by GraphPad Prism.