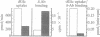Abstract
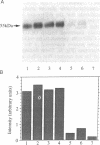
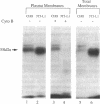
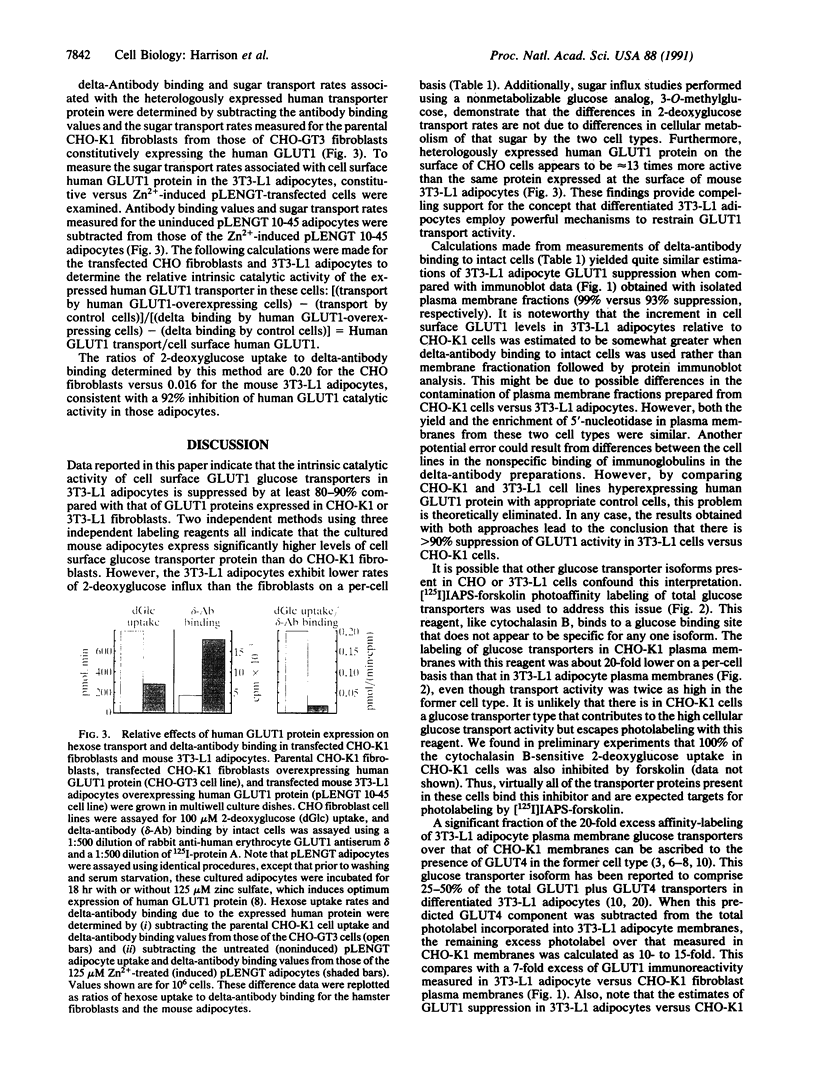
Previous studies indicated that the erythroidtype (GLUT1) glucose transporter isoform contributes to basal but not insulin-stimulated hexose transport in mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes. In the present studies it was found that basal hexose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes was about 50% lower than that in 3T3-L1 or CHO-K1 fibroblasts. Intrinsic catalytic activities of GLUT1 transporters in CHO-K1 and 3T3-L1 cells were compared by normalizing these hexose transport rates to GLUT1 content on the cell surface, as measured by two independent methods. Cell surface GLUT1 levels in 3T3-L1 fibroblasts and adipocytes were about 10- and 25-fold higher, respectively, than in CHO-K1 fibroblasts, as assessed with an anti-GLUT1 exofacial domain antiserum, delta. The large excess of cell surface GLUT1 transporters in 3T3-L1 adipocytes relative to CHO-K1 fibroblasts was confirmed by GLUT1 protein immunoblot analysis and by photoaffinity labelling (with 3-[125I]iodo-4-azidophenethylamido-7-O-succinyldeacetylforskoli n) of glucose transporters in isolated plasma membranes. Thus, GLUT1 intrinsic activity is markedly reduced in 3T3-L1 fibroblasts compared with the CHO-K1 fibroblasts, and further reduction occurs upon differentiation to adipocytes. Intrinsic catalytic activities specifically associated with heterologously expressed human GLUT1 protein in transfected CHO-K1 versus 3T3-L1 cells were determined by subtracting appropriate control cell values for hexose transport and delta-antibody binding from those determined in the transfected cells expressing high levels of human GLUT1. The results confirmed a greater than 90% inhibition of the intrinsic catalytic activity of human GLUT1 transporters on the surface of mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes relative to CHO-K1 fibroblasts. We conclude that a mechanism that markedly suppresses basal hexose transport catalyzed by GLUT1 is a major contributor to the dramatic insulin sensitivity of glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asano T., Shibasaki Y., Ohno S., Taira H., Lin J. L., Kasuga M., Kanazawa Y., Akanuma Y., Takaku F., Oka Y. Rabbit brain glucose transporter responds to insulin when expressed in insulin-sensitive Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3416–3420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J., Haspel H. C., Rosen O. M. Transformation of rat fibroblasts by FSV rapidly increases glucose transporter gene transcription. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1495–1498. doi: 10.1126/science.3029870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J. Identification of a novel gene encoding an insulin-responsive glucose transporter protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90968-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blok J., Gibbs E. M., Lienhard G. E., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J. Insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters from post-Golgi compartments to the plasma membrane of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):69–76. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderhead D. M., Lienhard G. E. Labeling of glucose transporters at the cell surface in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Evidence for both translocation and a second mechanism in the insulin stimulation of transport. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12171–12174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers A. ATP regulation of the human red cell sugar transporter. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11028–11037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers A. Anomalous asymmetric kinetics of human red cell hexose transfer: role of cytosolic adenosine 5'-triphosphate. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3592–3602. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers A. Facilitated diffusion of glucose. Physiol Rev. 1990 Oct;70(4):1135–1176. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.4.1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy B. M., Czech M. P. Hexose transport stimulation and membrane redistribution of glucose transporter isoforms in response to cholera toxin, dibutyryl cyclic AMP, and insulin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12434–12443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy B. M., Harrison S. A., Buxton J. M., Czech M. P. Protein synthesis inhibitors activate glucose transport without increasing plasma membrane glucose transporters in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10122–10130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Derechin V., James D. E., Tordjman K., Ahern S., Gibbs E. M., Lienhard G. E., Mueckler M. Insulin-stimulated translocation of the HepG2/erythrocyte-type glucose transporter expressed in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2180–2184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. A., Buxton J. M., Clancy B. M., Czech M. P. Insulin regulation of hexose transport in mouse 3T3-L1 cells expressing the human HepG2 glucose transporter. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20106–20116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. A., Buxton J. M., Helgerson A. L., MacDonald R. G., Chlapowski F. J., Carruthers A., Czech M. P. Insulin action on activity and cell surface disposition of human HepG2 glucose transporters expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5793–5801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert D. N., Carruthers A. Direct evidence for ATP modulation of sugar transport in human erythrocyte ghosts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10093–10099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman G. D., Kozka I. J., Clark A. E., Flower C. J., Saltis J., Habberfield A. D., Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Cell surface labeling of glucose transporter isoform GLUT4 by bis-mannose photolabel. Correlation with stimulation of glucose transport in rat adipose cells by insulin and phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18172–18179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Brown R., Navarro J., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulatable tissues express a unique insulin-sensitive glucose transport protein. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):183–185. doi: 10.1038/333183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Strube M., Mueckler M. Molecular cloning and characterization of an insulin-regulatable glucose transporter. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):83–87. doi: 10.1038/338083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joost H. G., Weber T. M., Cushman S. W., Simpson I. A. Activity and phosphorylation state of glucose transporters in plasma membranes from insulin-, isoproterenol-, and phorbol ester-treated rat adipose cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11261–11267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joost H. G., Weber T. M., Cushman S. W., Simpson I. A. Insulin-stimulated glucose transport in rat adipose cells. Modulation of transporter intrinsic activity by isoproterenol and adenosine. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10033–10036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Christy R. J., McLenithan J. C., Braiterman L. T., Cornelius P., Pekala P. H., Lane M. D. Sequence, tissue distribution, and differential expression of mRNA for a putative insulin-responsive glucose transporter in mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3150–3154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasanicki M. A., Pilch P. F. Regulation of glucose-transporter function. Diabetes Care. 1990 Mar;13(3):219–227. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Hormonal regulation of mammalian glucose transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1059–1089. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tordjman K. M., Leingang K. A., James D. E., Mueckler M. M. Differential regulation of two distinct glucose transporter species expressed in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: effect of chronic insulin and tolbutamide treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7761–7765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadzinski B. E., Shanahan M. F., Clark R. B., Ruoho A. E. Identification of the glucose transporter in mammalian cell membranes with a 125I-forskolin photoaffinity label. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 1;255(3):983–990. doi: 10.1042/bj2550983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadzinski B. E., Shanahan M. F., Ruoho A. E. Derivatization of the human erythrocyte glucose transporter using a novel forskolin photoaffinity label. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17683–17689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzano A., Wilkinson W., Kotliar N., Thoidis G., Wadzinkski B. E., Ruoho A. E., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulated glucose uptake in rat adipocytes is mediated by two transporter isoforms present in at least two vesicle populations. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12358–12363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]